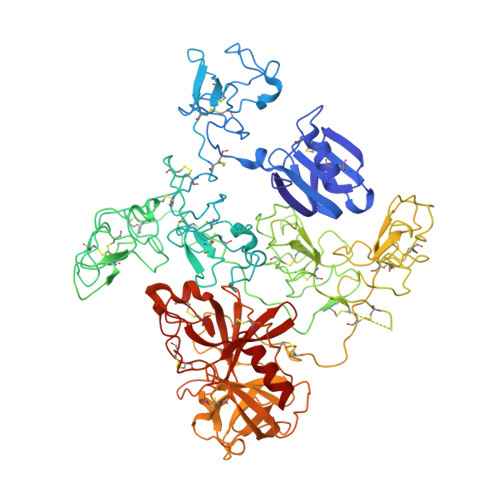
Crystal Structure of the Native Plasminogen Reveals an Activation-Resistant Compact Conformation.
Xue, Y., Bodin, C., Olsson, K.(2012) J Thromb Haemost 10: 1385
- PubMed: 22540246
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2012.04765.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4A5T - PubMed Abstract:
Plasminogen is the zymogen form of plasmin and the precursor of angiostatin. It has been implicated in a variety of disease states, including thrombosis, bleeding and cancers. The native plasminogen, known as Glu-plasminogen, contains seven domains comprising the N-terminal peptide domain (NTP), five kringle domains (K1-K5) and the C-terminal serine protease domain (SP). Previous studies have established that the lysine binding site (LBS) of the conserved kringle domains plays a crucial role in mediating the regulation of plasminogen function. However, details of the related conformational mechanism are unknown. We aim to understand in more detail the conformational mechanism of plasminogen activation involving the kringles. We crystallized the native plasminogen under physiologically relevant conditions and determined the structure at 3.5 Å resolution. We performed structural analyses and related these to the literature data to gain critical understanding of the plasminogen activation. The structure reveals the precise architecture of the quaternary complex. It shows that the Glu-plasminogen renders its compact form as an activation-resistant conformation for the proteolytic activation. The LBSs of all kringles, except K1, are engaged in intra-molecular interactions while only K1-LBS is readily available for ligand binding or receptor anchorage. The structure also provides insights into the interactions between plasminogen and α2-antiplasmin, the primary physiological inhibitor of plasmin. Furthermore, the data presented explain why a conformational transition to the open form is necessary for plasminogen activation as well as angiostatin generation, and provide a rationale for the functional hierarchy of the different kringles.
Organizational Affiliation:
Discovery Sciences, AstraZeneca R&D Mölndal, Mölndal, Sweden. yafeng.xue@astrazeneca.com