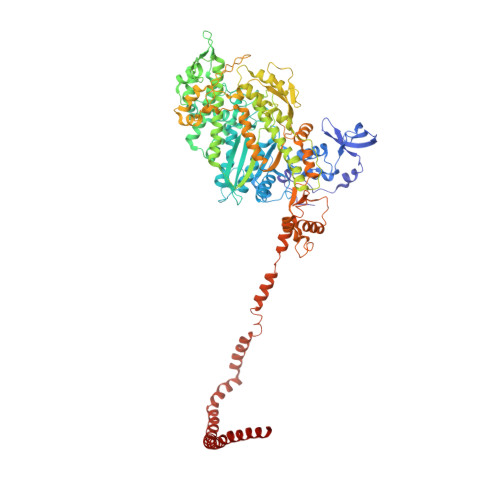
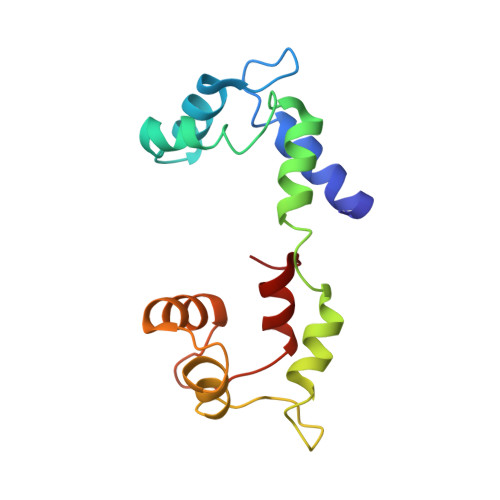
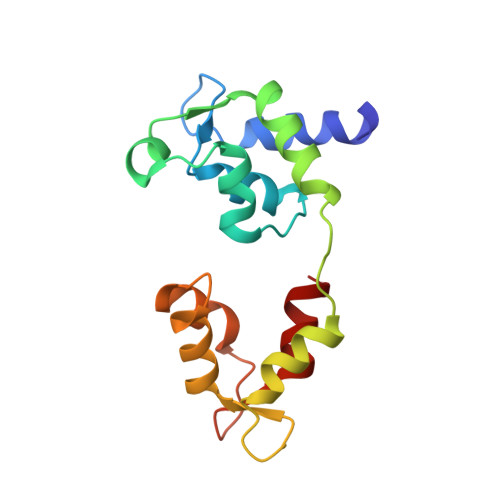
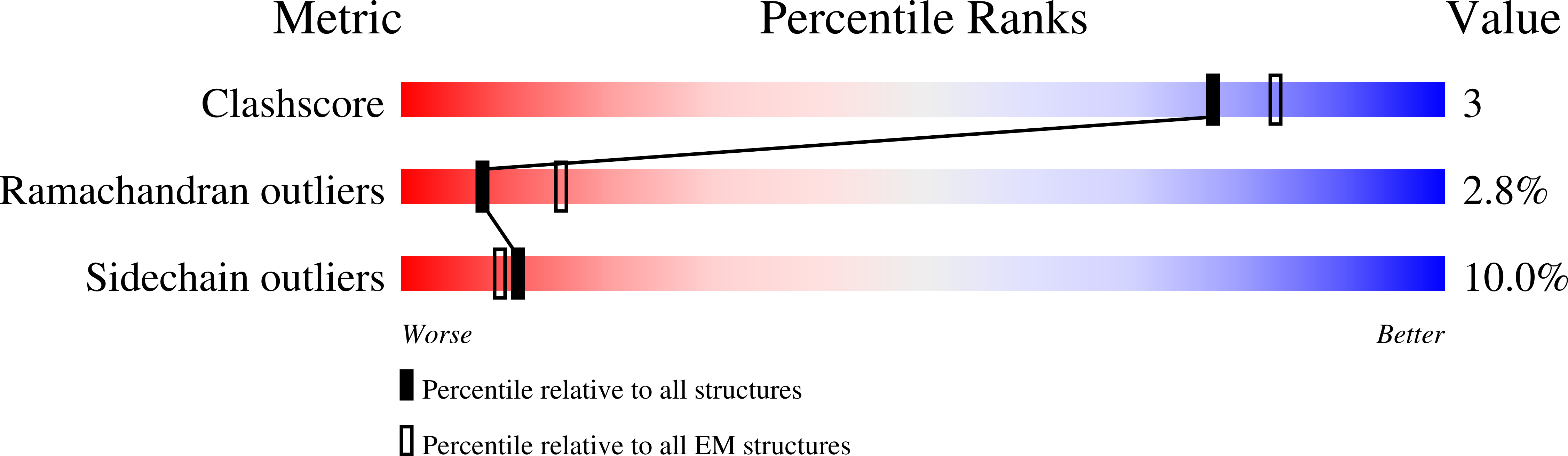Phosphorylated smooth muscle heavy meromyosin shows an open conformation linked to activation.
Baumann, B.A., Taylor, D.W., Huang, Z., Tama, F., Fagnant, P.M., Trybus, K.M., Taylor, K.A.(2012) J Mol Biol 415: 274-287
- PubMed: 22079364
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2011.10.047
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3J04 - PubMed Abstract:
Smooth muscle myosin and smooth muscle heavy meromyosin (smHMM) are activated by regulatory light chain phosphorylation, but the mechanism remains unclear. Dephosphorylated, inactive smHMM assumes a closed conformation with asymmetric intramolecular head-head interactions between motor domains. The "free head" can bind to actin, but the actin binding interface of the "blocked head" is involved in interactions with the free head. We report here a three-dimensional structure for phosphorylated, active smHMM obtained using electron crystallography of two-dimensional arrays. Head-head interactions of phosphorylated smHMM resemble those found in the dephosphorylated state but occur between different molecules, not within the same molecule. The light chain binding domain structure of phosphorylated smHMM differs markedly from that of the "blocked" head of dephosphorylated smHMM. We hypothesize that regulatory light chain phosphorylation opens the inhibited conformation primarily by its effect on the blocked head. Singly phosphorylated smHMM is not compatible with the closed conformation if the blocked head is phosphorylated. This concept has implications for the extent of myosin activation at low levels of phosphorylation in smooth muscle.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Molecular Biophysics, Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL 32306, USA.