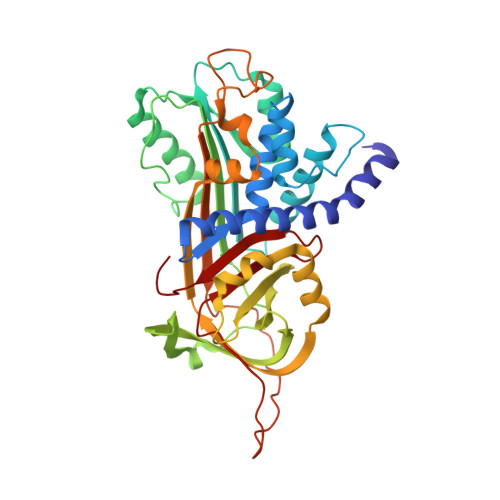
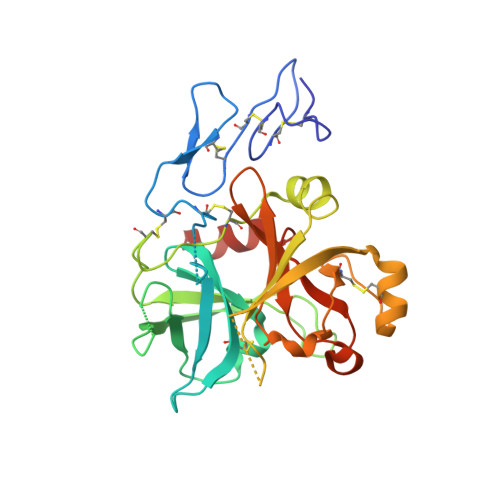
Crystal structure of protein Z-dependent inhibitor complex shows how protein Z functions as a cofactor in the membrane inhibition of factor X.
Wei, Z., Yan, Y., Carrell, R.W., Zhou, A.(2009) Blood
- PubMed: 19528533
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-04-210021
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3F1S - PubMed Abstract:
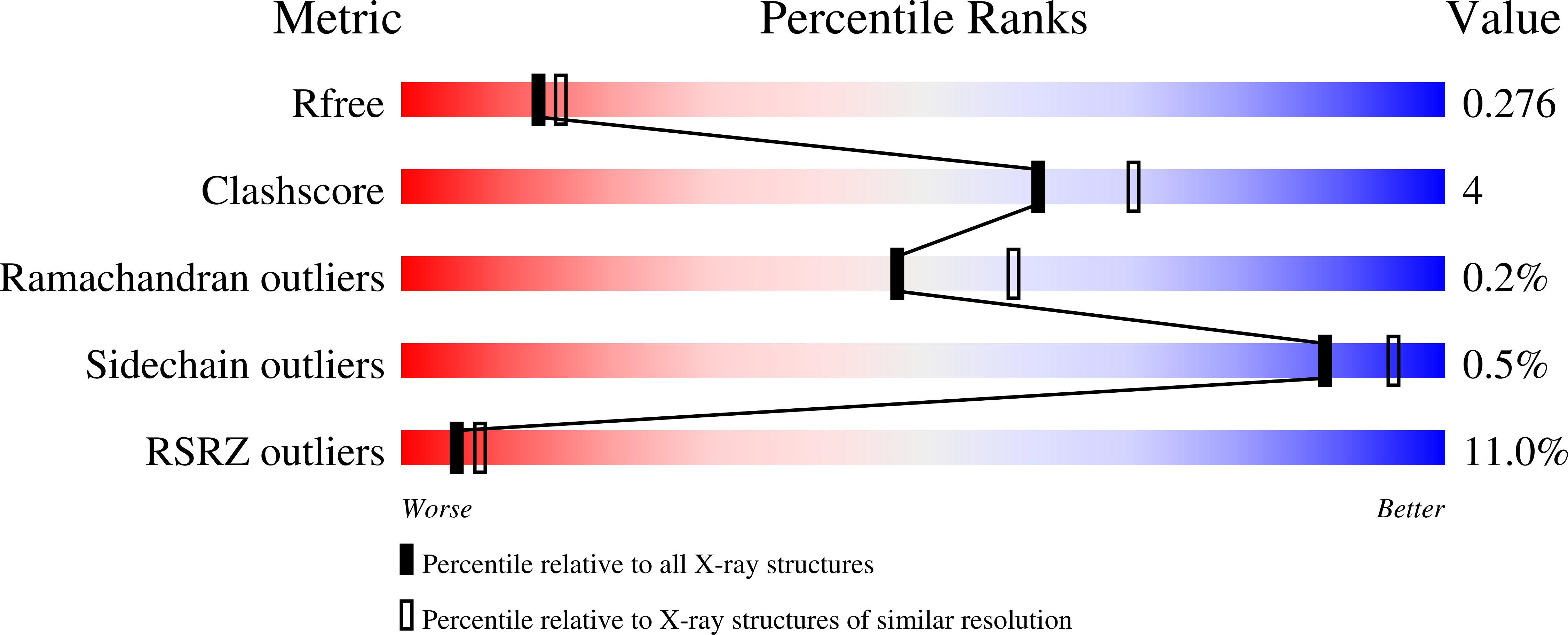
Protein Z (PZ) binds to PZ-dependent inhibitor (ZPI) and accelerates the inhibition of the coagulation protease, activated factor X (FXa), in the presence of phospholipids and Ca2+. A 2.3A resolution crystal structure of PZ complexed with ZPI shows that ZPI is a typical serine protease inhibitor and that PZ has a serine protease fold with distorted oxyanion hole and S1 pocket. The 2 molecules bind with fully complementary surfaces spanning over 2400A(2) and involving extensive ionic and hydrophobic interactions. ZPI has an unusual shutter region with a negatively charged residue buried within the hydrophobic core of the molecule. This unique Asp(213) is critical in maintaining the balanced metastability required for optimal protease inhibition, especially when PZ is bound, with its replacement with Asn resulting in increased thermal stability, but decreased efficiency of protease inhibition. The structure of ZPI shows negatively and positively charged surfaces on top of the molecule, in keeping with mutagenesis studies in this work indicating exosite interactions with FXa when it docks on top of ZPI. As modeled in this study, the gamma-carboxy-glutamic acid-containing domains of PZ and FXa enable them to bind to the same phospholipid surfaces on platelet and other membranes, with optimal proximity for the inhibition of FXa by the complexed ZPI.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Haematology, University of Cambridge, Cambridge Institute for Medical Research, Cambridge, United Kingdom.