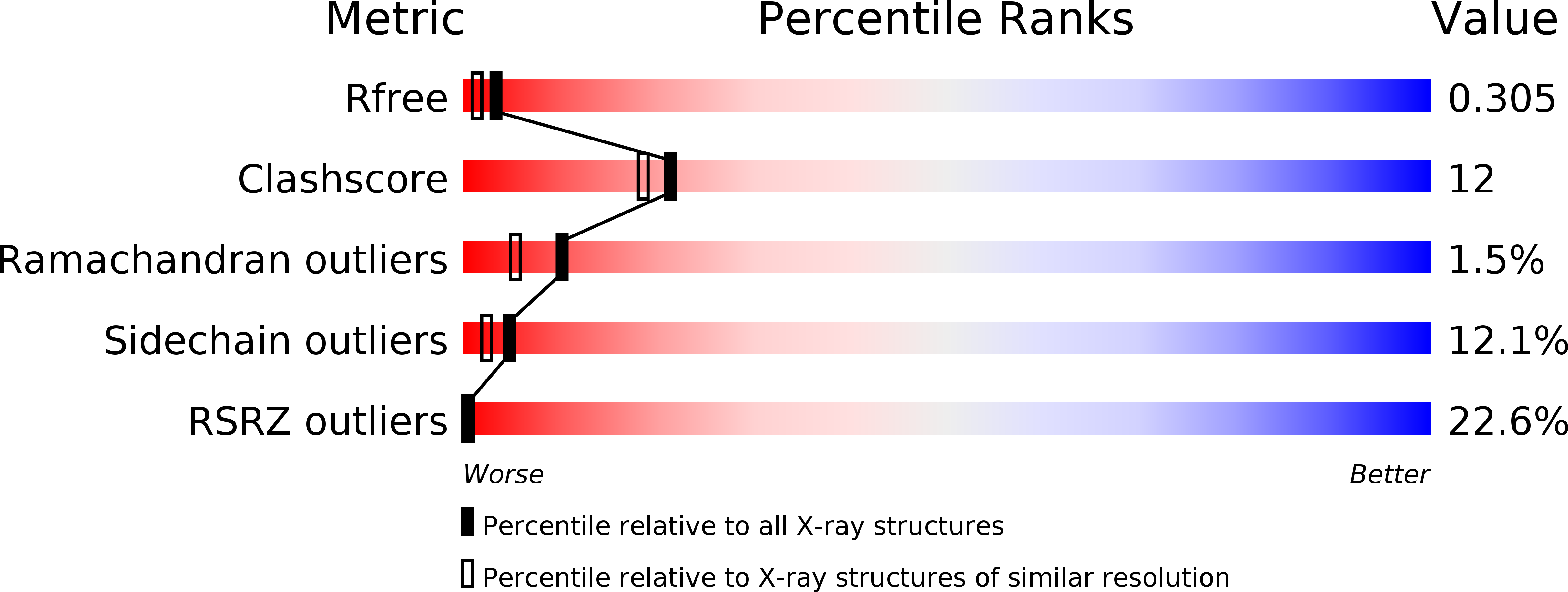
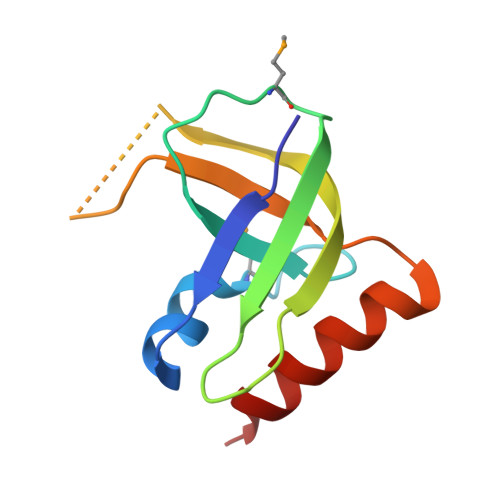
XC1028 from Xanthomonas campestris adopts a PilZ domain-like structure without a c-di-GMP switch.
Li, T.N., Chin, K.H., Liu, J.H., Wang, A.H., Chou, S.H.(2009) Proteins 75: 282-288
- PubMed: 19127589
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.22330
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3DSG - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of XC1028 from Xanthomonas campestris has been determined to a resolution of 2.15 A using the multiple anomalous dispersion approach. It bears significant sequence identity and similarity values of 64.10% and 70.09%, respectively, with PA2960, a protein indispensable for type IV pilus-mediated twitching motility, after which the PilZ motif was first named. However, both XC1028 and PA2960 lack detectable c-di-GMP binding capability. Although XC1028 adopts a structure comprising a five-stranded beta-barrel core similar to other canonical PilZ domains with robust c-di-GMP binding ability, considerable differences are observed in the N-terminal motif; XC1028 assumes a compact five-stranded beta-barrel without an extra long N-terminal motif, whereas other canonical PilZ domains contain a long N-terminal sequence embedded with an essential "c-di-GMP switch" motif. In addition, a beta-strand (beta1) in the N-terminal motif, running in exactly opposite polarity to that of XC1028, is found inserted into the parallel beta3/beta1' strands, forming a completely antiparallel beta4 downward arrow beta3 upward arrow beta1 downward arrow beta1' upward arrow sheet in the canonical PilZ domains. Such dramatic structural differences at the N-terminus may account for the diminished c-di-GMP binding capability of XC1028, and suggest that interactions with additional proteins are necessary to bind c-di-GMP for type IV fimbriae assembly.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Biochemistry, National Chung-Hsing University, Taichung, 40227, Taiwan, Republic of China.