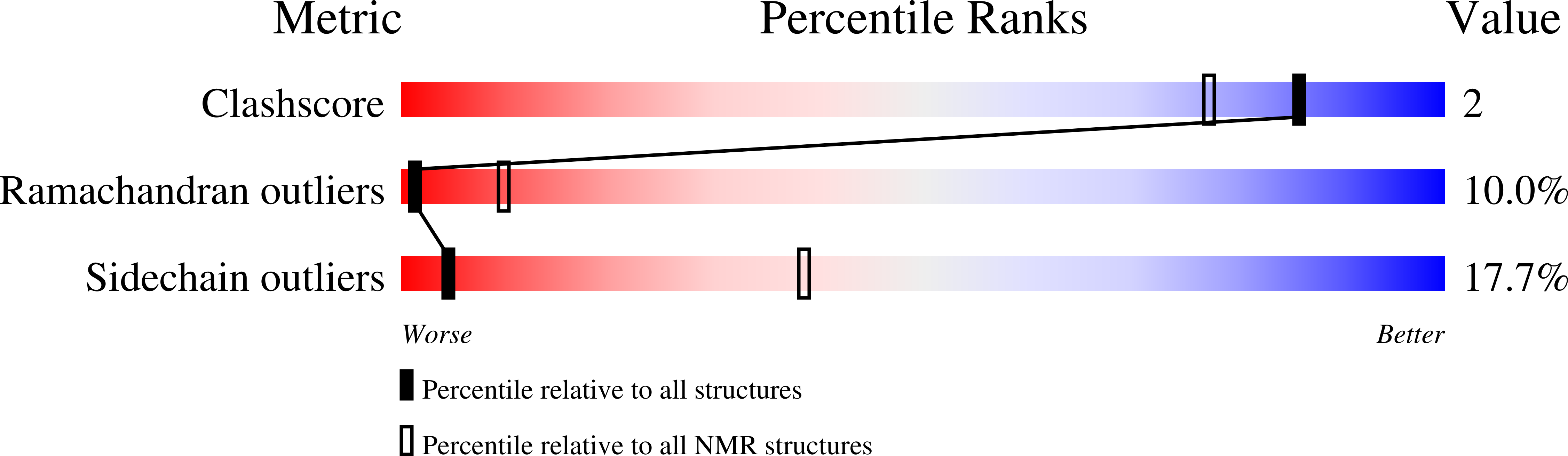Insights into tyrosine phosphorylation control of protein-protein association from the NMR structure of a band 3 peptide inhibitor bound to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Eisenmesser, E.Z., Post, C.B.(1998) Biochemistry 37: 867-877
- PubMed: 9454576
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi971445b
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3BTB - PubMed Abstract:
A protein-protein association regulated by phosphorylation of tyrosine is examined by NMR structural studies and biochemical studies. Binding of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (G3PDH) and aldolase to the N-terminus of human erythrocyte anion transporter, band 3, inhibits enzyme activity. This inhibition is reversed upon phosphorylation of band 3 Y8, as shown by kinetic studies on purified components, as well as in vivo studies. Thus, tyrosine phosphorylation mediates against the intermolecular protein-protein association, in contrast to the positive control involving SH2 and PTB domains where phosphorylation is required for binding. To elucidate the basis of recognition and negative control by tyrosine phosphorylation, the structure of a synthetic peptide, B3P, corresponding to the first 15 residues of band 3 (MEELQDDYEDMMEEN-NH2), bound to G3PDH has been determined using the exchange-transferred nuclear Overhauser effect. The G3PDH-bound B3P structure was found to be very similar to the structure recognized by aldolase. A hydrophobic triad forms from side chains within a loop structure of residues 4 through 9 in both bound species. Another structural feature stabilizing the loop, in the case of the B3P-G3PDH complex, is a hydrogen bond between the side chains of Y8 and D10 associated with a beta-turn of residues 8-11. Based on the structure of this phosphorylation sensitive interaction (PSI) loop, it is suggested that tyrosine phosphorylation disrupts protein-protein association, in part, by intramolecular electrostatic destabilization. The inhibition by B3P is competitive with respect to the coenzyme NAD+ and noncompetitive with the substrate analog arsenate. Specific binding of B3P to G3PDH is demonstrated by reversion of the NMR spectral properties of bound B3P to those of the free peptide upon addition of coenzyme and substrate analog. The stoichiometry of binding for the B3P-G3PDH complex was determined from Sephadex G-50 displacement experiments to be 4:1. Collectively, these results are consistent with B3P binding the active site of G3PDH.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana 47907-1392, USA.