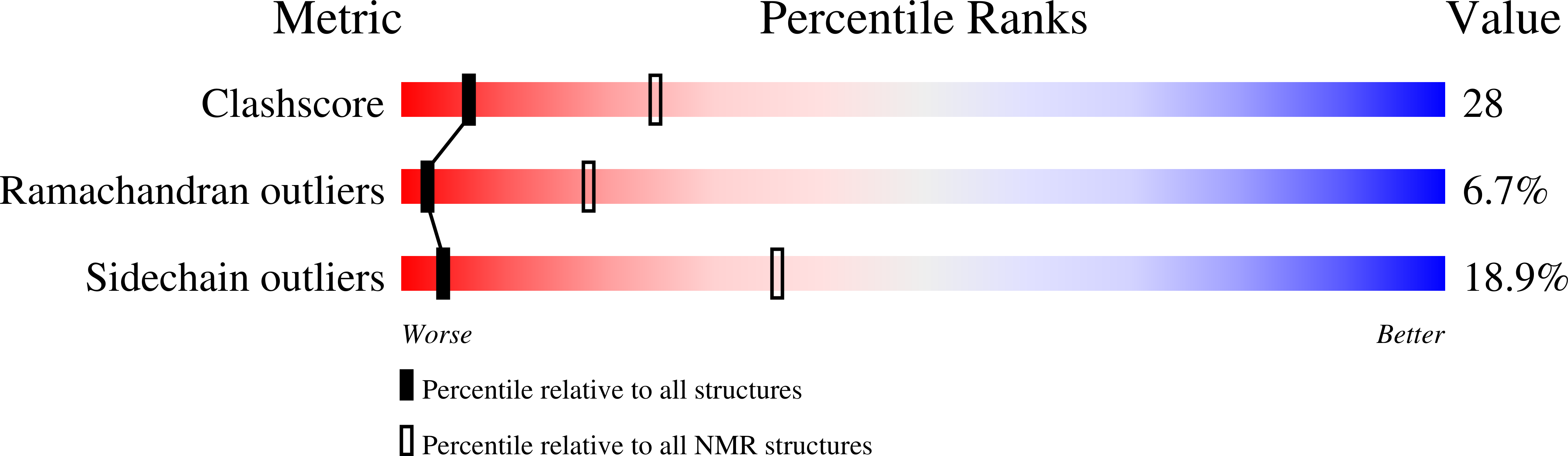NMR structure of DREAM: Implications for Ca(2+)-dependent DNA binding and protein dimerization.
Lusin, J.D., Vanarotti, M., Li, C., Valiveti, A., Ames, J.B.(2008) Biochemistry 47: 2252-2264
- PubMed: 18201103
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi7017267
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2JUL - PubMed Abstract:
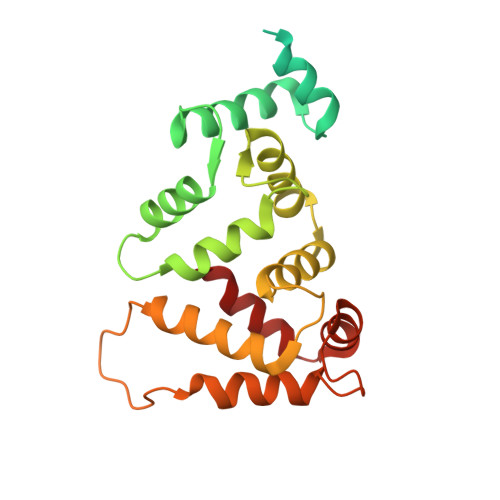
DREAM (calsenilin/KChIP3) is an EF-hand calcium-binding protein that binds to specific DNA sequences and regulates Ca2+-induced transcription of prodynorphin and c-fos genes. Here, we present the atomic-resolution structure of Ca2+-bound DREAM in solution determined by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. Pulsed-field gradient NMR diffusion experiments and 15N NMR relaxation analysis indicate that Ca2+-bound DREAM forms a stable dimer in solution. The structure of the first 77 residues from the N-terminus could not be determined by our NMR analysis. The C-terminal DREAM structure (residues 78-256) contains four EF-hand motifs arranged in a tandem linear array, similar to that seen in KChIP1, recoverin, and other structures of the neuronal calcium sensor (NCS) branch of the calmodulin superfamily. Mg2+ is bound at the second EF-hand, whereas Ca2+ is bound functionally at the third and fourth sites. The first and second EF-hands form an exposed hydrophobic groove on the protein surface lined by side-chain atoms of L96, F100, F114, I117, Y118, F121, F122, Y151, L155, L158, and L159 that are highly conserved in all NCS proteins. An exposed leucine near the C-terminus (L251) is suggested to form intermolecular contacts with leucine residues in the hydrophobic groove (L155, L158, and L159). Positively charged side chains of Arg and Lys (Lys87, Lys90, Lys91, Arg98, Lys101, Arg160, and Lys166) are clustered on one side of the protein surface and may mediate electrostatic contacts with DNA targets. We propose that Ca2+-induced dimerization of DREAM may partially block the putative DNA-binding site, which may suggest as to how Ca2+ abolishes DREAM binding to DNA to activate the transcription of prodynorphin and other downstream genes in pain control.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, University of California, Davis, California 95616, USA.