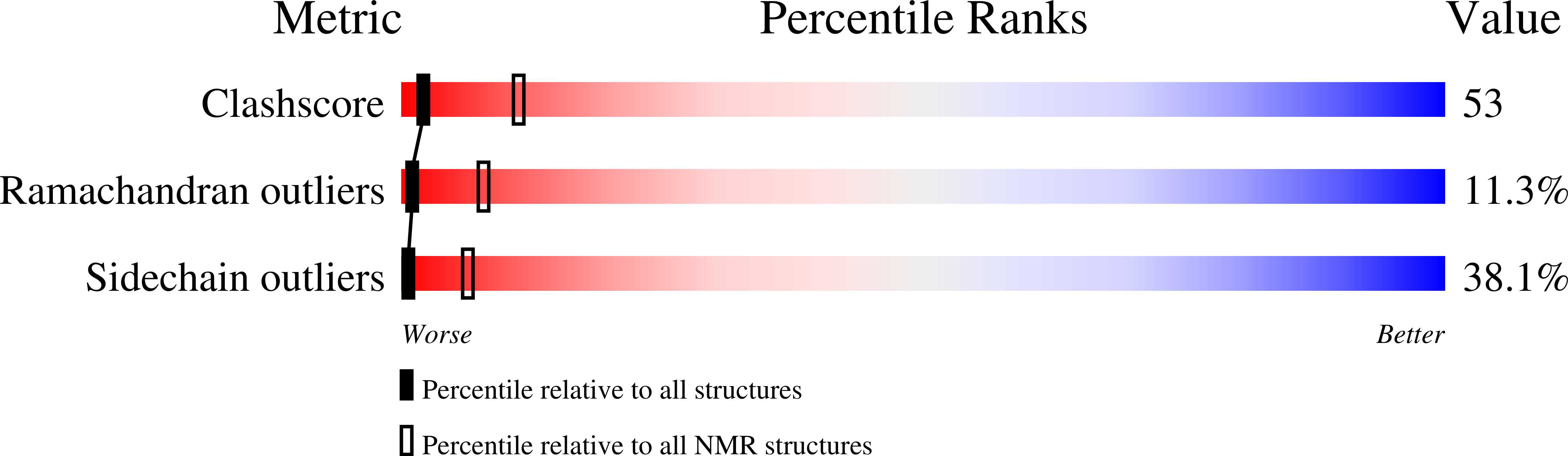Solution Structure and Alanine Scan of a Spider Toxin That Affects the Activation of Mammalian Voltage-gated Sodium Channels
Corzo, G., Sabo, J.K., Bosmans, F., Billen, B., Villegas, E., Tytgat, J., Norton, R.S.(2007) J Biol Chem 282: 4643-4652
- PubMed: 17148449
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M605403200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2GX1 - PubMed Abstract:
Magi 5, from the hexathelid spider Macrothele gigas, is a 29-residue polypeptide containing three disulfide bridges. It binds specifically to receptor site 4 on mammalian voltage-gated sodium channels and competes with scorpion beta-toxins, such as Css IV from Centruroides suffusus suffusus. As a consequence, Magi 5 shifts the activation voltage of the mammalian rNav1.2a channel to more hyperpolarized voltages, whereas the insect channel, DmNav1, is not affected. To gain insight into toxin-channel interactions, Magi 5 and 23 analogues were synthesized. The three-dimensional structure of Magi 5 in aqueous solution was determined, and its voltage-gated sodium channel-binding surfaces were mapped onto this structure using data from electrophysiological measurements on a series of Ala-substituted analogues. The structure clearly resembles the inhibitor cystine knot structural motif, although the triple-stranded beta-sheet typically found in that motif is partially distorted in Magi 5. The interactive surface of Magi 5 toward voltage-gated sodium channels resembles in some respects the Janus-faced atracotoxins, with functionally important charged residues on one face of the toxin and hydrophobic residues on the other. Magi 5 also resembles the scorpion beta-toxin Css IV, which has distinct nonpolar and charged surfaces that are critical for channel binding and has a key Glu involved in voltage sensor trapping. These two distinct classes of toxin, with different amino acid sequences and different structures, may utilize similar groups of residues on their surface to achieve the common end of modifying voltage-gated sodium channel function.
Organizational Affiliation:
Instituto de Biotecnologi´a, Universidad Nacional Auto´noma de México, Apartado Postal 510-3, Cuernavaca, Morelos 61500, Mexico; Suntory Institute for Bioorganic Research, Mishima-gun, Shimamoto-cho, Wakayamadai 1-1-1, Osaka 618-8503, Japan.