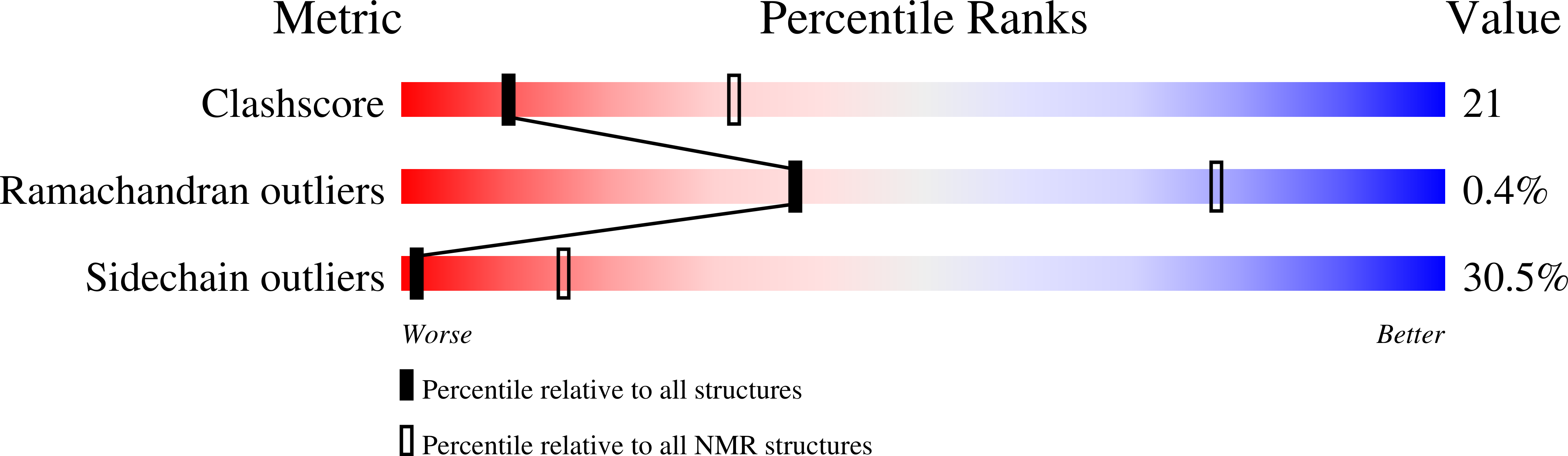Structure of a Novel P-Superfamily Spasmodic Conotoxin Reveals an Inhibitory Cystine Knot Motif
Miles, L.A., Dy, C.Y., Nielsen, J., Barnham, K.J., Hinds, M.G., Olivera, B.M., Bulaj, G., Norton, R.S.(2002) J Biol Chem 277: 43033-43040
- PubMed: 12193600
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M206690200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1IXT - PubMed Abstract:
Conotoxin gm9a, a putative 27-residue polypeptide encoded by Conus gloriamaris, was recently identified as a homologue of the "spasmodic peptide", tx9a, isolated from the venom of the mollusk-hunting cone shell Conus textile (Lirazan, M. B., Hooper, D., Corpuz, G. P., Ramilo, C. A., Bandyopadhyay, P., Cruz, L. J., and Olivera, B. M. (2000) Biochemistry 39, 1583-1588). The C. gloriamaris spasmodic peptide has been synthesized, and the refolded polypeptide was shown to be biologically active using a mouse bioassay. The chemically synthesized gm9a elicited the same symptomatology described previously for natively folded tx9a, and gm9a and tx9a were of similar potency, implying that neither the two gamma-carboxyglutamate (Gla) residues found in tx9a (Ser(8) and Ala(13) in gm9a) nor Gly(1) (Ser(1) in gm9a) are crucial for biological activity. We have determined the three-dimensional structure of gm9a in aqueous solution and demonstrated that the molecule adopts the well known inhibitory cystine knot motif constrained by three disulfide bonds involving Cys(2)-Cys(16), Cys(6)-Cys(18) and Cys(12)-Cys(23). Based on the gm9a structure, the sites of Gla substitution in tx9a are in loops located on one surface of the molecule, which is unlikely to be involved directly in receptor binding. Because this is the first structure reported for a member of the newly defined P-superfamily conotoxins, a comparison has been made with structurally related conotoxins. This shows that the structural scaffold that characterizes the P-conotoxins has the greatest potential for exhibiting structural diversity among the robust inhibitory cystine knot-containing conotoxins, a finding that has implications for functional epitope mimicry and protein engineering.
Organizational Affiliation:
The Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research, NMR Laboratory, 381 Royal Parade, Parkville 3052, Australia.