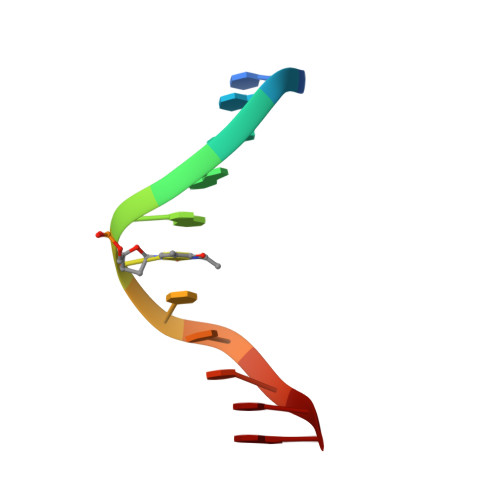
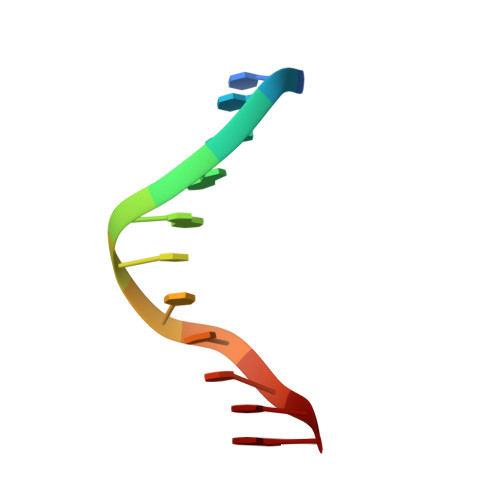
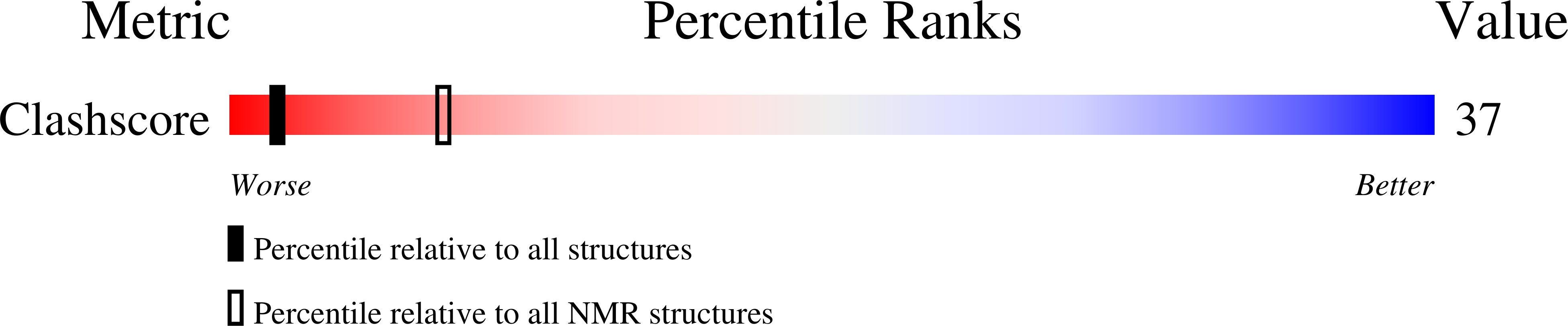Accommodation of mispair aligned N3T-ethyl-N3T DNA interstrand cross link.
da Silva, M.W., Wilds, C.J., Noronha, A.M., Colvin, O.M., Miller, P.S., Gamcsik, M.P.(2004) Biochemistry 43: 12549-12554
- PubMed: 15449944
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0486435
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1S37 - PubMed Abstract:
The solution structure of the undecamer d(CGAAATTTTCG)(2), where T represents a N(3)T-ethyl-N(3)T interstrand cross link, was elucidated using molecular dynamics calculations restrained by NOE and dihedral data obtained from NMR spectroscopy. The ethyl moiety is particularly well-accommodated between the minor and major grooves. This is an exceptional example of the plasticity along the axis defined by the stem and a unique finding of an interstrand cross link occupying the area associating minor and major grooves. The mismatch-aligned tethered bases preserve good intrastrand stacking with flanking bases. Base-pair steps adjacent to the lesion site are overwound. Accommodation of the lesion also results in an increase in mispair staggering alignment modulated by flexibility because of the tetrahedral geometry of the exocyclic ethyl carbon atoms. This is mechanically coupled with a small measure of concomitant propeller twisting without an increase in intrastrand base-step distance. Both x displacement and sugar puckering are indicative of canonical B DNA throughout the stem. We have thus established that the lesion defined by mismatch-aligned minor groove N(3)T-ethyl-N(3)T cross-linked thymine bases produces very localized distortions in a DNA stem that may be difficult to recognize by repair mechanisms that are not transcription- or replication-coupled. Thus, this synthetic DNA is a valuable structural probe to study mechanisms of repair.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Medicine, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina 27710, USA.