Kinetic Constraints in the Specific Interaction between Phosphorylated Ubiquitin and Proteasomal Shuttle Factors.
Qin, L.Y., Gong, Z., Liu, K., Dong, X., Tang, C.(2021) Biomolecules 11
- PubMed: 34356632
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11071008
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
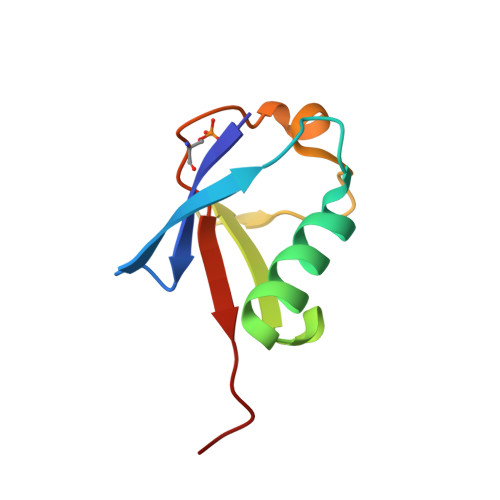
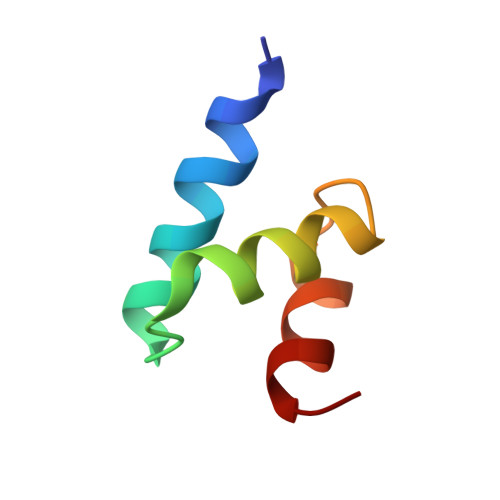
7F7X - PubMed Abstract:
Ubiquitin (Ub) specifically interacts with the Ub-associating domain ( UBA ) in a proteasomal shuttle factor, while the latter is involved in either proteasomal targeting or self-assembly coacervation. PINK1 phosphorylates Ub at S65 and makes Ub alternate between C-terminally relaxed ( pUb RL ) and retracted conformations ( pUb RT ). Using NMR spectroscopy, we show that pUb RL but not pUb RT preferentially interacts with the UBA from two proteasomal shuttle factors Ubqln2 and Rad23A. Yet discriminatorily, Ubqln2- UBA binds to pUb more tightly than Rad23A does and selectively enriches pUb RL upon complex formation. Further, we determine the solution structure of the complex between Ubqln2- UBA and pUb RL and uncover the thermodynamic basis for the stronger interaction. NMR kinetics analysis at different timescales further suggests an indued-fit binding mechanism for pUb-UBA interaction. Notably, at a relatively low saturation level, the dissociation rate of the UBA-pUb RL complex is comparable with the exchange rate between pUb RL and pUb RT . Thus, a kinetic constraint would dictate the interaction between Ub and UBA , thus fine-tuning the functional state of the proteasomal shuttle factors.
- Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan 430071, China.
Organizational Affiliation: