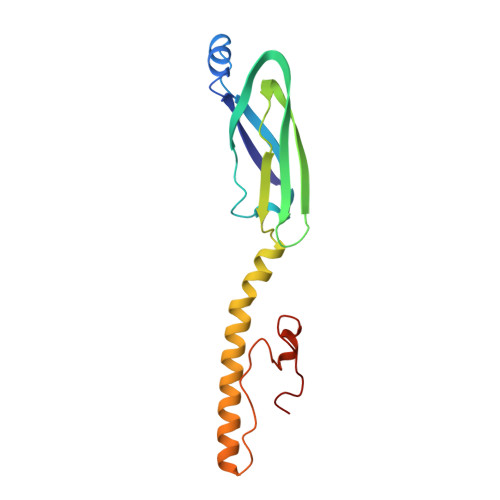
A Flexible and Original Architecture of Two Unrelated Zinc Fingers Underlies the Role of the Multitask P1 in RYMV Spread.
Poignavent, V., Hoh, F., Terral, G., Yang, Y., Gillet, F.X., Kim, J.H., Allemand, F., Lacombe, E., Brugidou, C., Cianferani, S., Demene, H., Vignols, F.(2022) J Mol Biology 434: 167715-167715
- PubMed: 35798161
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2022.167715
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6TY0, 6TY2, 6XV2 - PubMed Abstract:
Viruses of the sobemovirus genus are plant viruses, most of which generate very important agricultural and financial losses. Among them, the rice yellow mottle virus (RYMV) is one of the most damaging pathogens devastating rice fields in Africa. RYMV infectivity and propagation rely on its protein P1, identified as a key movement and potential long-distance RNA silencing suppressor. Here we describe P1's complete 3D structure and dynamics obtained by an integrative approach combining X-Ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy. We show that P1 is organized in two semi-independent and topologically unrelated domains, each harboring an original zinc finger. The two domains exhibit different affinities for zinc and sensitivities to oxidoreduction conditions, making the C-terminal P1 region a potential labile sensor of the plant redox status. An additional level of regulation resides on the capacity of P1 to oligomerize through its N-terminal domain. Coupling P1 structure information with site-directed mutagenesis and plant functional assays, we identified key residues in each zinc domain essential for infectivity and spread in rice tissues. Altogether, our results provide the first complete structure of a sobemoviral P1 movement protein and highlight structural and dynamical properties that may serve RYMV functions to infect and invade its host plant.
- IPME, Université de Montpellier, IRD, CIRAD, Montpellier, France; IBMP, Univ Strasbourg, CNRS, Strasbourg, France.
Organizational Affiliation: