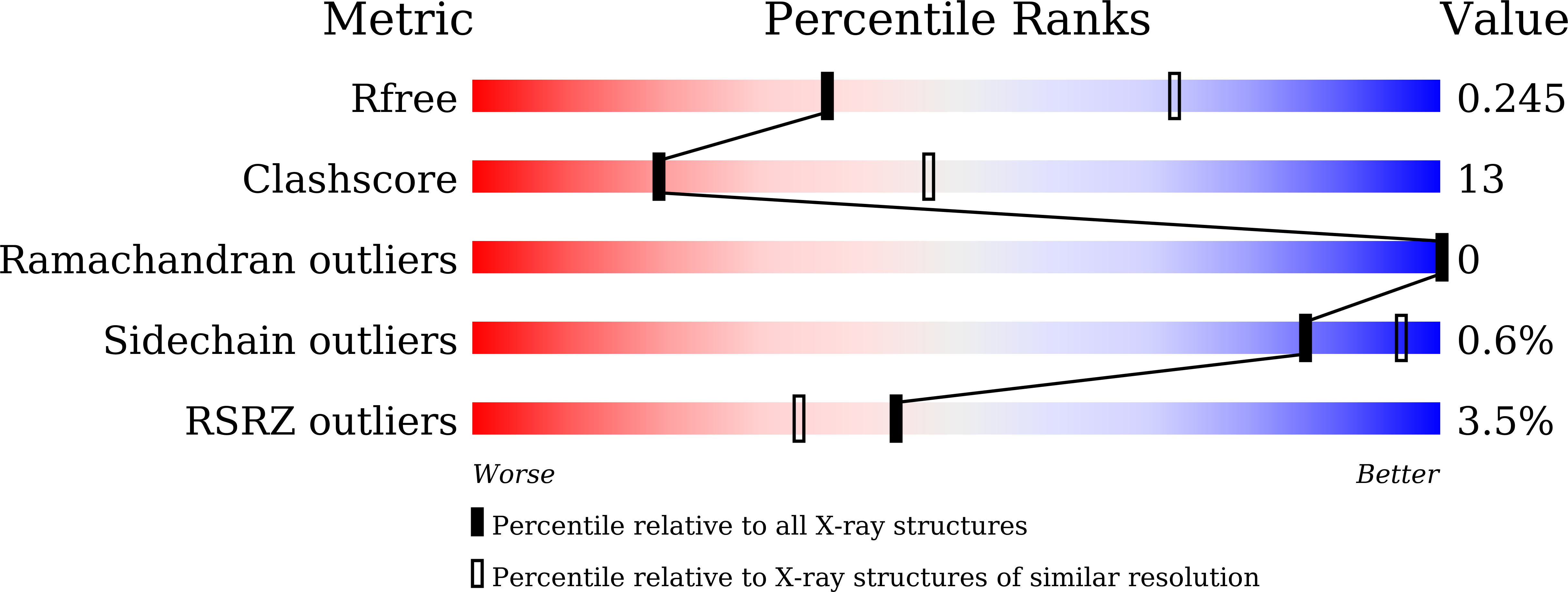
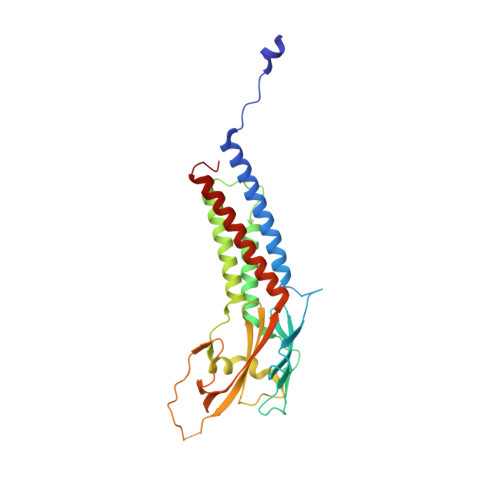
The crystal structure of human Rogdi provides insight into the causes of Kohlschutter-Tonz Syndrome
Lee, H., Jeong, H., Choe, J., Jun, Y., Lim, C., Lee, C.(2017) Sci Rep 7: 3972-3972
- PubMed: 28638151
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-04120-x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5XQH, 5XQI - PubMed Abstract:
Kohlschutter-Tönz syndrome (KTS) is a rare autosomal-recessive disorder of childhood onset characterized by global developmental delay, spasticity, epilepsy, and amelogenesis imperfecta. Rogdi, an essential protein, is highly conserved across metazoans, and mutations in Rogdi are linked to KTS. However, how certain mutations in Rogdi abolish its physiological functions and cause KTS is not known. In this study, we determined the crystal structure of human Rogdi protein at atomic resolution. Rogdi forms a novel elongated curved structure comprising the α domain, a leucine-zipper-like four-helix bundle, and a characteristic β-sheet domain. Within the α domain, the N-terminal H1 helix (residues 19-45) pairs with the C-terminal H6 helix (residues 252-287) in an antiparallel manner, indicating that the integrity of the four-helix bundle requires both N- and C-terminal residues. The crystal structure, in conjunction with biochemical data, indicates that the α domain might undergo a conformational change and provide a structural platform for protein-protein interactions. Disruption of the four-helix bundle by mutation results in significant destabilization of the structure. This study provides structural insights into how certain mutations in Rogdi affect its structure and cause KTS, which has important implications for the development of pharmaceutical agents against this debilitating neurological disease.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences, School of Life Sciences, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, 50 UNIST-gil, Ulsan, 44919, Republic of Korea.