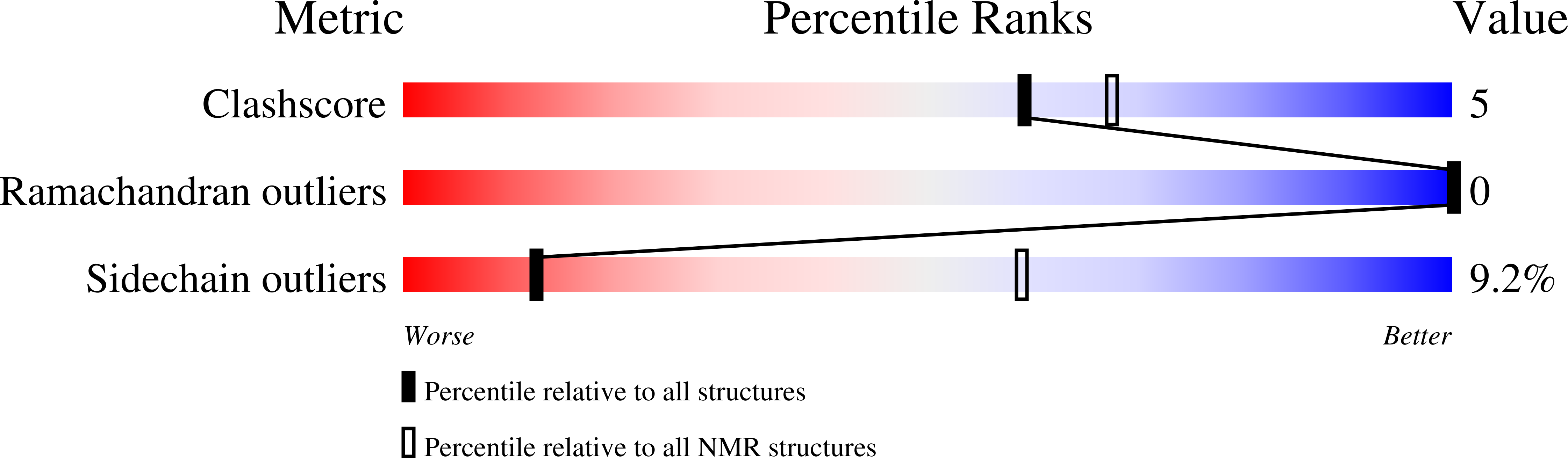Novel venom-derived inhibitors of the human EAG channel, a putative antiepileptic drug target.
Ma, L., Chin, Y.K.Y., Dekan, Z., Herzig, V., Chow, C.Y., Heighway, J., Lam, S.W., Guillemin, G.J., Alewood, P.F., King, G.F.(2018) Biochem Pharmacol 158: 60-72
- PubMed: 30149017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2018.08.038
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5WLX - PubMed Abstract:
Recently, we and other groups revealed that gain-of-function mutations in the human ether à go-go voltage-gated potassium channel hEAG1 (K v 10.1) lead to developmental disorders with associated infantile-onset epilepsy. However, the physiological role of hEAG1 in the central nervous system remains elusive. Potent and selective antagonists of hEAG1 are therefore much sought after, both as pharmacological tools for studying the (patho)physiological functions of this enigmatic channel and as potential leads for development of anti-epileptic drugs. Since animal venoms are a rich source of potent ion channel modifiers that have been finely tuned by millions of year of evolution, we screened 108 arachnid venoms for hEAG1 inhibitors using electrophysiology. Two hit peptides (Aa1a and Ap1a) were isolated, sequenced, and chemically synthesised for structure-function studies. Both of these hEAG1 inhibitors are C-terminally amidated peptides containing an inhibitor cystine knot motif, which provides them with exceptional stability in both plasma and cerebrospinal fluid. Aa1a and Ap1a are the most potent peptidic inhibitors of hEAG1 reported to date, and they present a novel mode of action by targeting both the activation and inactivation gating of the channel. These peptides should be useful pharmacological tools for probing hEAG1 function as well as informative leads for the development of novel anti-epileptic drugs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute for Molecular Bioscience, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, QLD 4072, Australia. Electronic address: linlin.ma@flinders.edu.au.