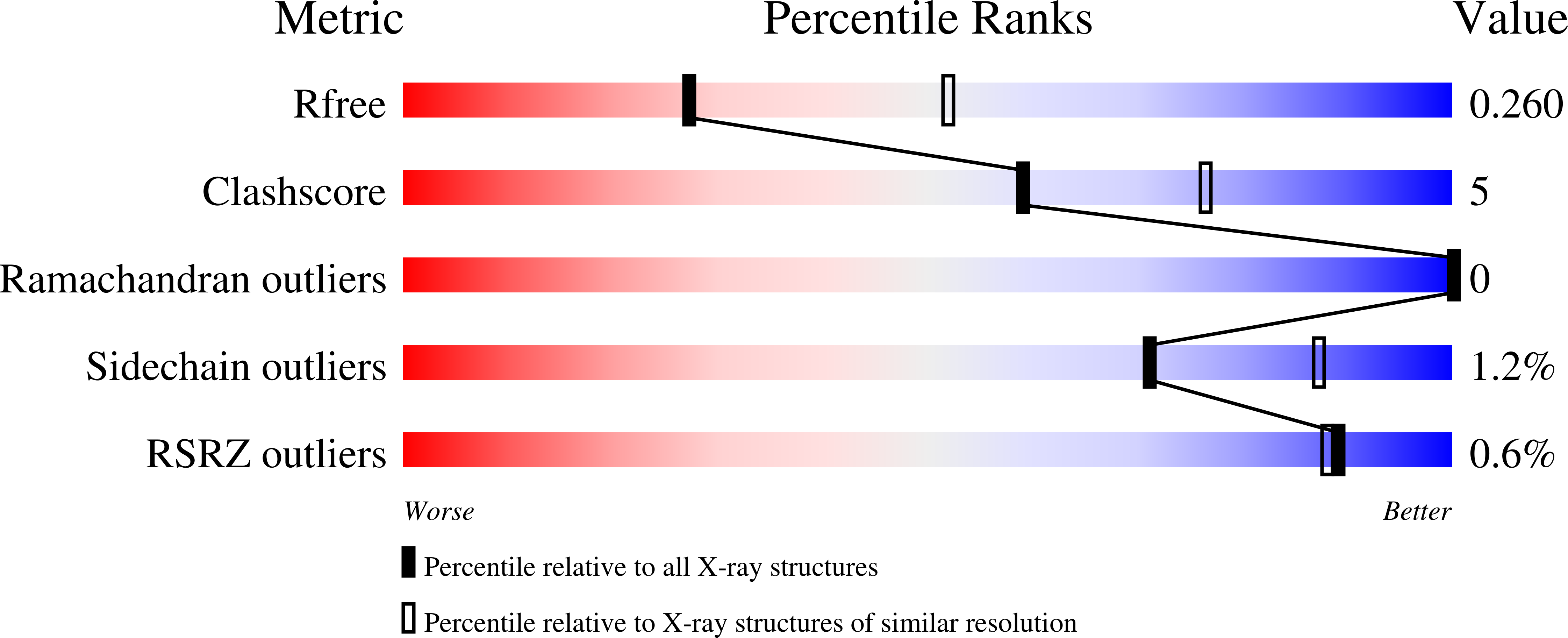
Protein S-Bacillithiolation Functions in Thiol Protection and Redox Regulation of the Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Gap in Staphylococcus aureus Under Hypochlorite Stress.
Imber, M., Huyen, N.T.T., Pietrzyk-Brzezinska, A.J., Loi, V.V., Hillion, M., Bernhardt, J., Tharichen, L., Kolsek, K., Saleh, M., Hamilton, C.J., Adrian, L., Grater, F., Wahl, M.C., Antelmann, H.(2018) Antioxid Redox Signal 28: 410-430
- PubMed: 27967218
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2016.6897
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5T73 - PubMed Abstract:
Bacillithiol (BSH) is the major low-molecular-weight thiol of the human pathogen Staphylococcus aureus. In this study, we used OxICAT and Voronoi redox treemaps to quantify hypochlorite-sensitive protein thiols in S. aureus USA300 and analyzed the role of BSH in protein S-bacillithiolation. The OxICAT analyses enabled the quantification of 228 Cys residues in the redox proteome of S. aureus USA300. Hypochlorite stress resulted in >10% increased oxidation of 58 Cys residues (25.4%) in the thiol redox proteome. Among the highly oxidized sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl)-sensitive proteins are five S-bacillithiolated proteins (Gap, AldA, GuaB, RpmJ, and PpaC). The glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P) dehydrogenase Gap represents the most abundant S-bacillithiolated protein contributing 4% to the total Cys proteome. The active site Cys151 of Gap was very sensitive to overoxidation and irreversible inactivation by hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ) or NaOCl in vitro. Treatment with H 2 O 2 or NaOCl in the presence of BSH resulted in reversible Gap inactivation due to S-bacillithiolation, which could be regenerated by the bacilliredoxin Brx (SAUSA300_1321) in vitro. Molecular docking was used to model the S-bacillithiolated Gap active site, suggesting that formation of the BSH mixed disulfide does not require major structural changes. Conclusion and Innovation: Using OxICAT analyses, we identified 58 novel NaOCl-sensitive proteins in the pathogen S. aureus that could play protective roles against the host immune defense and include the glycolytic Gap as major target for S-bacillithiolation. S-bacillithiolation of Gap did not require structural changes, but efficiently functions in redox regulation and protection of the active site against irreversible overoxidation in S. aureus. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 28, 410-430.
Organizational Affiliation:
1 Institute for Biology-Microbiology, Freie Universität Berlin , Berlin, Germany .