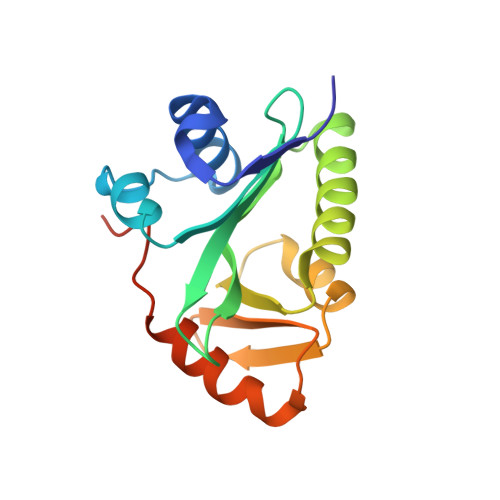
Crystal structure of the N-acetyltransferase domain of human N-acetyl-L-glutamate synthase in complex with N-acetyl-L-glutamate provides insights into its catalytic and regulatory mechanisms.
Zhao, G., Jin, Z., Allewell, N.M., Tuchman, M., Shi, D.(2013) PLoS One 8: e70369-e70369
- PubMed: 23894642
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0070369
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4K30 - PubMed Abstract:
N-acetylglutamate synthase (NAGS) catalyzes the conversion of AcCoA and L-glutamate to CoA and N-acetyl-L-glutamate (NAG), an obligate cofactor for carbamyl phosphate synthetase I (CPSI) in the urea cycle. NAGS deficiency results in elevated levels of plasma ammonia which is neurotoxic. We report herein the first crystal structure of human NAGS, that of the catalytic N-acetyltransferase (hNAT) domain with N-acetyl-L-glutamate bound at 2.1 Å resolution. Functional studies indicate that the hNAT domain retains catalytic activity in the absence of the amino acid kinase (AAK) domain. Instead, the major functions of the AAK domain appear to be providing a binding site for the allosteric activator, L-arginine, and an N-terminal proline-rich motif that is likely to function in signal transduction to CPS1. Crystalline hNAT forms a dimer similar to the NAT-NAT dimers that form in crystals of bifunctional N-acetylglutamate synthase/kinase (NAGS/K) from Maricaulis maris and also exists as a dimer in solution. The structure of the NAG binding site, in combination with mutagenesis studies, provide insights into the catalytic mechanism. We also show that native NAGS from human and mouse exists in tetrameric form, similar to those of bifunctional NAGS/K.
Organizational Affiliation:
Center for Genetic Medicine Research and Department of Integrative Systems Biology, Children's National Medical Center, The George Washington University, Washington, DC, United States of America.