Structure and Function of AvtR, a Novel Transcriptional Regulator from a Hyperthermophilic Archaeal Lipothrixvirus.
Peixeiro, N., Keller, J., Collinet, B., Leulliot, N., Campanacci, V., Cortez, D., Cambillau, C., Nitta, K.R., Vincentelli, R., Forterre, P., Prangishvili, D., Sezonov, G., van Tilbeurgh, H.(2013) J Virol 87: 124-136
- PubMed: 23055559
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01306-12
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
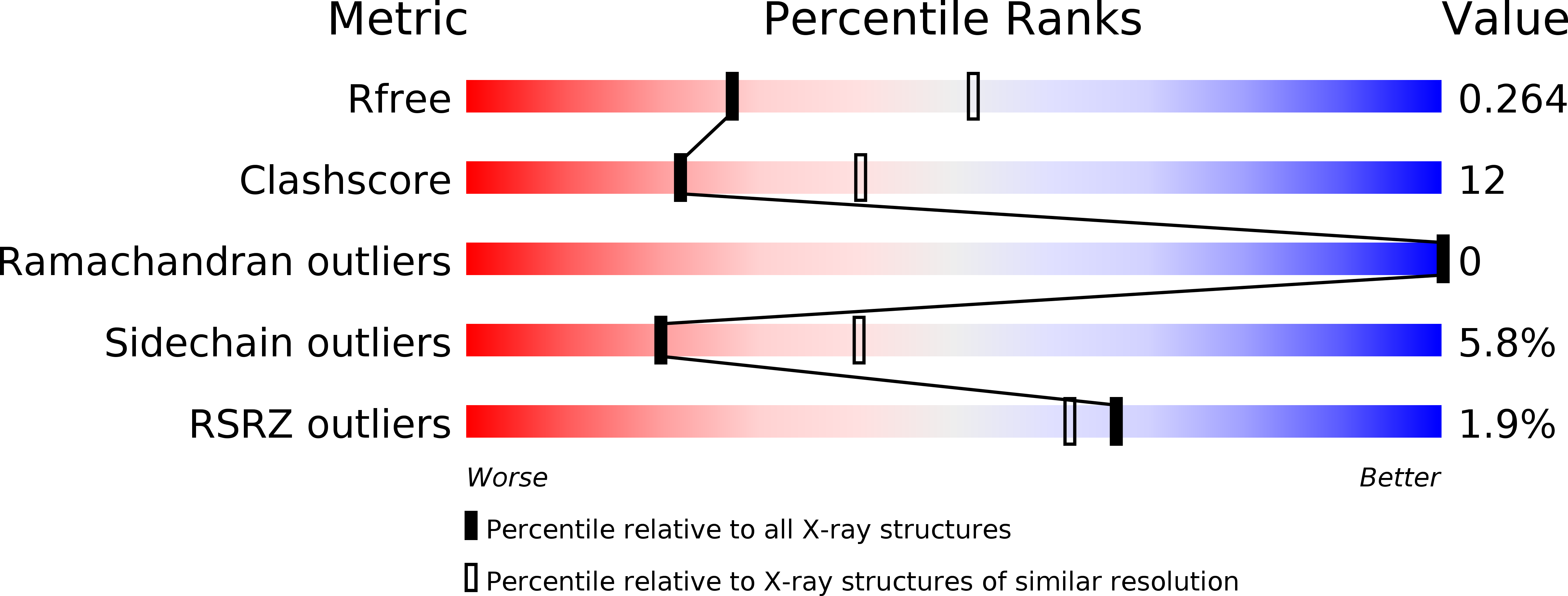
4HV0 - PubMed Abstract:
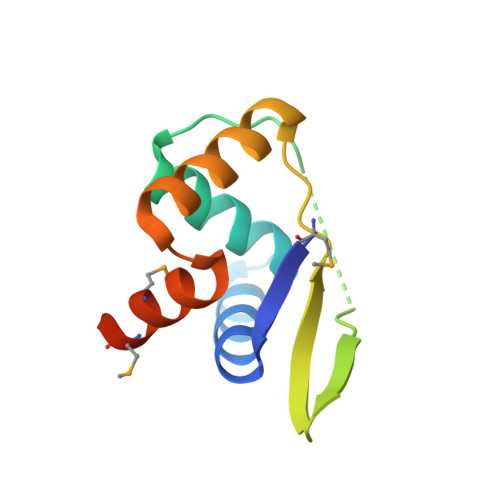
The structural and functional analysis of the protein AvtR encoded by Acidianus filamentous virus 6 (AFV6), which infects the archaeal genus Acidianus, revealed its unusual structure and involvement in transcriptional regulation of several viral genes. The crystal structure of AvtR (100 amino acids) at 2.6-Å resolution shows that it is constituted of a repeated ribbon-helix-helix (RHH) motif, which is found in a large family of bacterial transcriptional regulators. The known RHH proteins form dimers that interact with DNA using their ribbon to create a central β-sheet. The repeated RHH motifs of AvtR superpose well on such dimers, but its central sheet contains an extra strand, suggesting either conformational changes or a different mode of DNA binding. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (SELEX) experiments combined with systematic mutational and computational analysis of the predicted site revealed 8 potential AvtR targets in the AFV6 genome. Two of these targets were studied in detail, and the complex role of AvtR in the transcriptional regulation of viral genes was established. Repressing transcription from its own gene, gp29, AvtR can also act as an activator of another gene, gp30. Its binding sites are distant from both genes' TATA boxes, and the mechanism of AvtR-dependent regulation appears to include protein oligomerization starting from the protein's initial binding sites. Many RHH transcriptional regulators of archaeal viruses could share this regulatory mechanism.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institut Pasteur, Unité Biologie Moléculaire du Gène chez les Extrémophiles, Département de Microbiologie, Paris, France.