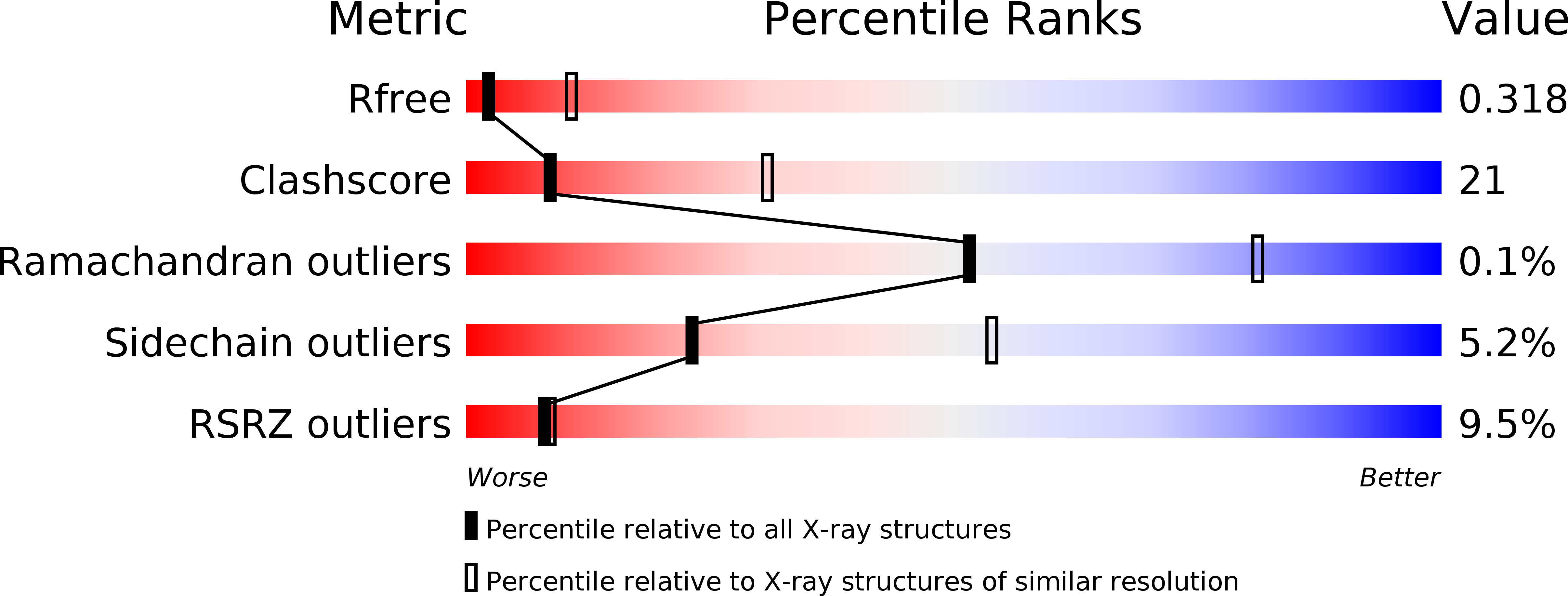
X-ray structures of eIF5B and the eIF5B-eIF1A complex: the conformational flexibility of eIF5B is restricted on the ribosome by interaction with eIF1A
Zheng, A., Yu, J., Yamamoto, R., Ose, T., Tanaka, I., Yao, M.(2014) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 70: 3090-3098
- PubMed: 25478828
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1399004714021476
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3WBI, 3WBJ, 3WBK - PubMed Abstract:
eIF5B and eIF1A are two translation-initiation factors that are universally conserved among all kingdoms. They show a unique interaction in eukaryotes which is important for ribosomal subunit joining. Here, the structures of two isolated forms of yeast eIF5B and of the eIF5B-eIF1A complex (eIF1A and eIF5B do not contain the respective N-terminal domains) are reported. The eIF5B-eIF1A structure shows that the C-terminal tail of eIF1A binds to eIF5B domain IV, while the core domain of eIF1A is invisible in the electron-density map. Although the individual domains in all structures of eIF5B or archaeal IF5B (aIF5B) are similar, their domain arrangements are significantly different, indicating high structural flexibility, which is advantageous for conformational change during ribosomal subunit joining. Based on these structures, models of eIF5B, eIF1A and tRNAi(Met) on the 80S ribosome were built. The models suggest that the interaction between the eIF1A C-terminal tail and eIF5B helps tRNAi(Met) to bind to eIF5B domain IV, thus preventing tRNAi(Met) dissociation, stabilizing the interface for subunit joining and providing a checkpoint for correct ribosome assembly.
Organizational Affiliation:
Graduate School of Life Sciences, Hokkaido University, Kita 10 Nishi 8 Kita-Ku, Sapporo, Hokkaido 060-0810, Japan.