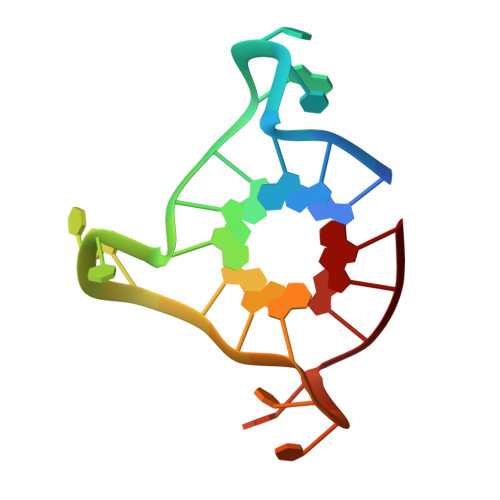
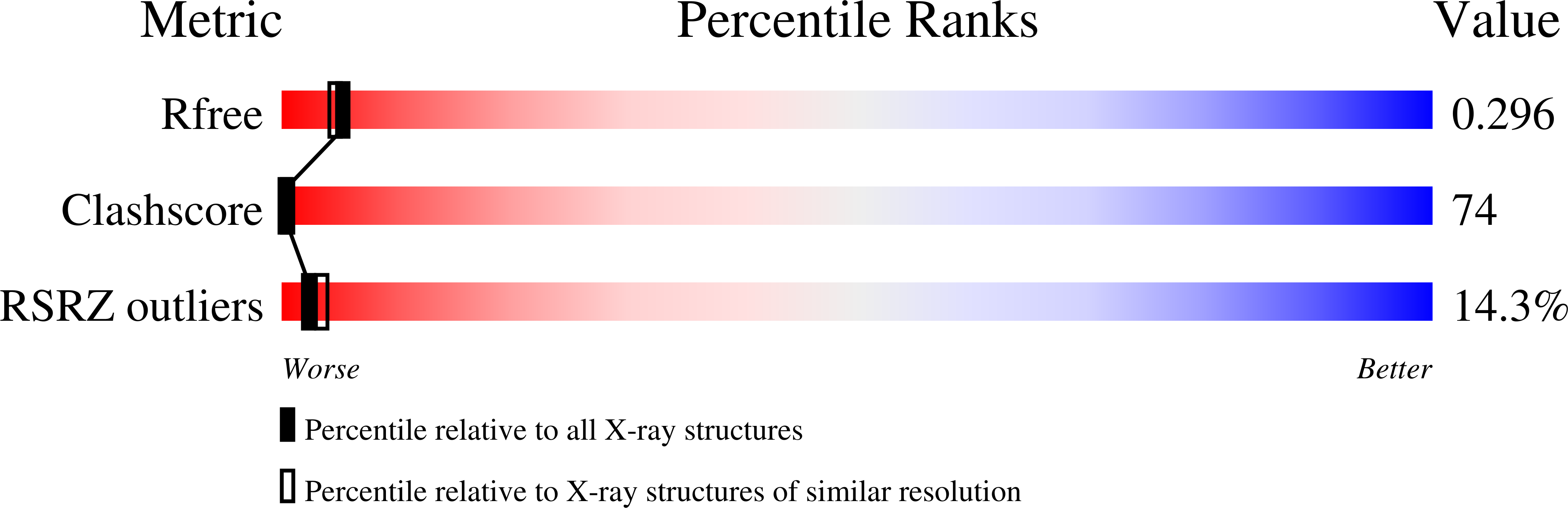Structural basis for telomeric g-quadruplex targeting by naphthalene diimide ligands.
Collie, G.W., Promontorio, R., Hampel, S.M., Micco, M., Neidle, S., Parkinson, G.N.(2012) J Am Chem Soc 134: 2723-2731
- PubMed: 22280460
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja2102423
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3SC8, 3T5E - PubMed Abstract:
The folding of the single-stranded 3' end of the human telomere into G-quadruplex arrangements inhibits the overhang from hybridizing with the RNA template of telomerase and halts telomere maintenance in cancer cells. The ability to thermally stabilize human telomeric DNA as a four-stranded G-quadruplex structure by developing selective small molecule compounds is a therapeutic path to regulating telomerase activity and thereby selectively inhibit cancer cell growth. The development of compounds with the necessary selectivity and affinity to target parallel-stranded G-quadruplex structures has proved particularly challenging to date, relying heavily upon limited structural data. We report here on a structure-based approach to the design of quadruplex-binding ligands to enhance affinity and selectivity for human telomeric DNA. Crystal structures have been determined of complexes between a 22-mer intramolecular human telomeric quadruplex and two potent tetra-substituted naphthalene diimide compounds, functionalized with positively charged N-methyl-piperazine side-chains. These compounds promote parallel-stranded quadruplex topology, binding exclusively to the 3' surface of each quadruplex. There are significant differences between the complexes in terms of ligand mobility and in the interactions with quadruplex grooves. One of the two ligands is markedly less mobile in the crystal complex and is more quadruplex-stabilizing, forming multiple electrostatic/hydrogen bond contacts with quadruplex phosphate groups. The data presented here provides a structural rationale for the biophysical (effects on quadruplex thermal stabilization) and biological data (inhibition of proliferation in cancer cell lines and evidence of in vivo antitumor activity) on compounds in this series and, thus, for the concept of telomere targeting with DNA quadruplex-binding small molecules.
Organizational Affiliation:
CRUK Biomolecular Structure Group, The School of Pharmacy, University of London, London, WC1N 1AX, United Kingdom.