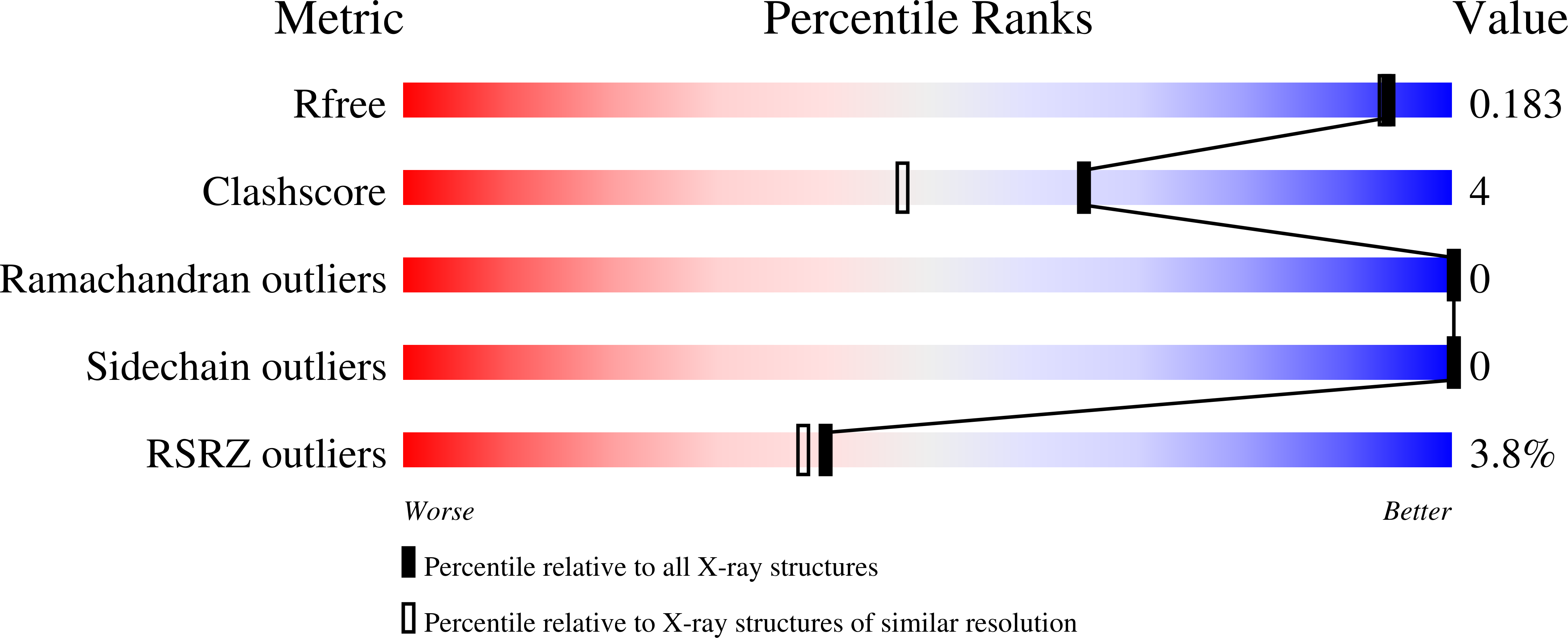
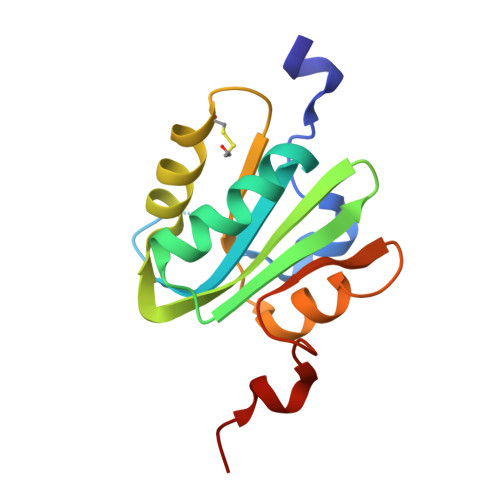
Structure-based analysis of the interaction between the simian virus 40 T-antigen origin binding domain and single-stranded DNA.
Meinke, G., Phelan, P.J., Fradet-Turcotte, A., Bohm, A., Archambault, J., Bullock, P.A.(2011) J Virol 85: 818-827
- PubMed: 20980496
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01738-10
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3QK2, 5D9I - PubMed Abstract:
The origin-binding domain (OBD) of simian virus 40 (SV40) large T-antigen (T-Ag) is essential for many of T-Ag's interactions with DNA. Nevertheless, many important issues related to DNA binding, for example, how single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) transits along the T-Ag OBD, have yet to be established. Therefore, X-ray crystallography was used to determine the costructure of the T-Ag OBD bound to DNA substrates such as the single-stranded region of a forked oligonucleotide. A second structure of the T-Ag OBD crystallized in the presence of poly(dT)(12) is also reported. To test the conclusions derived from these structures, residues identified as being involved in binding to ssDNA by crystallography or by an earlier nuclear magnetic resonance study were mutated, and their binding to DNA was characterized via fluorescence anisotropy. In addition, these mutations were introduced into full-length T-Ag, and these mutants were tested for their ability to support replication. When considered in terms of additional homology-based sequence alignments, our studies refine our understanding of how the T-Ag OBDs encoded by the polyomavirus family interact with ssDNA, a critical step during the initiation of DNA replication.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Tufts University School of Medicine, 136 Harrison Avenue, Boston, MA 02111, USA.