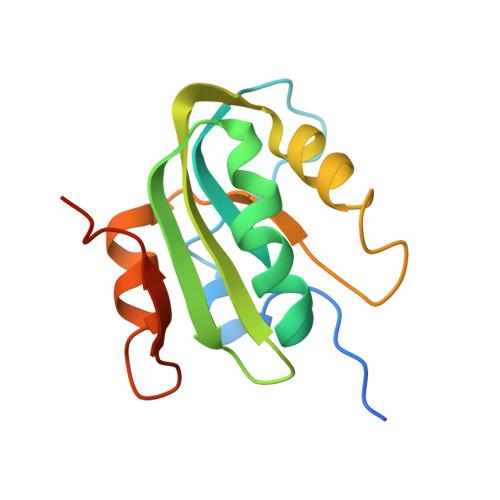
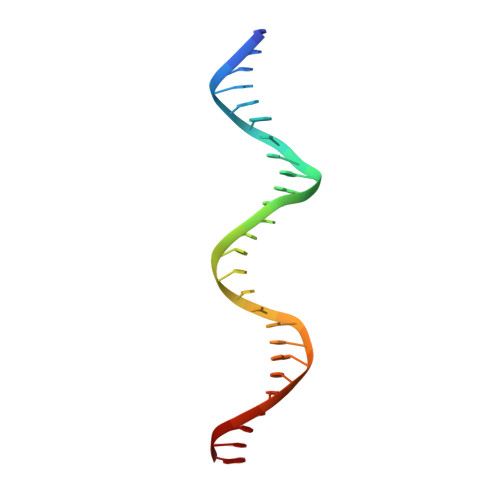
Asymmetric assembly of merkel cell polyomavirus large T-antigen origin binding domains at the viral origin.
Harrison, C.J., Meinke, G., Kwun, H.J., Rogalin, H., Phelan, P.J., Bullock, P.A., Chang, Y., Moore, P.S., Bohm, A.(2011) J Mol Biol 409: 529-542
- PubMed: 21501625
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2011.03.051
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3QFQ - PubMed Abstract:
The double-stranded DNA polyomavirus Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCV) causes Merkel cell carcinoma, an aggressive but rare human skin cancer that most often affects immunosuppressed and elderly persons. As in other polyomaviruses, the large T-antigen of MCV recognizes the viral origin of replication by binding repeating G(A/G)GGC pentamers. The spacing, number, orientation, and necessity of repeats for viral replication differ, however, from other family members such as SV40 and murine polyomavirus. We report here the 2.9 Å crystal structure of the MCV large T-antigen origin binding domain (OBD) in complex with a DNA fragment from the MCV origin of replication. Consistent with replication data showing that three of the G(A/G)GGC-like binding sites near the center of the origin are required for replication, the crystal structure contains three copies of the OBD. This stoichiometry was verified using isothermal titration calorimetry. The affinity for G(A/G)GGC-containing double-stranded DNA was found to be ~740 nM, approximately 8-fold weaker than the equivalent domain in SV40 for the analogous region of the SV40 origin. The difference in affinity is partially attributable to DNA-binding residue Lys331 (Arg154 in SV40). In contrast to SV40, a small protein-protein interface is observed between MCV OBDs when bound to the central region of the origin. This protein-protein interface is reminiscent of that seen in bovine papilloma virus E1 protein. Mutational analysis indicates, however, that this interface contributes little to DNA binding energy.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Sackler School of Graduate Biomedical Sciences, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston, MA 02111, USA.