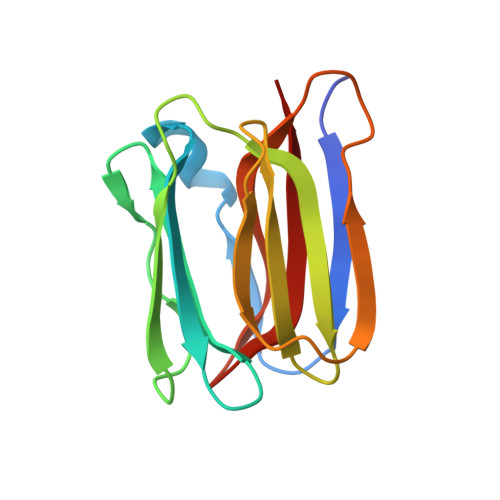
Crystal structures of human secretory proteins ZG16p and ZG16b reveal a Jacalin-related beta-prism fold
Kanagawa, M., Satoh, T., Ikeda, A., Nakano, Y., Yagi, H., Kato, K., Kojima-Aikawa, K., Yamaguchi, Y.(2010) Biochem Biophys Res Commun
- PubMed: 21110947
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.11.093
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3APA, 3AQG - PubMed Abstract:
ZG16p is a secretory protein that mediates condensation-sorting of pancreatic enzymes to the zymogen granule membrane in pancreatic acinar cells. ZG16p interacts with glycosaminoglycans and the binding is considered to be important for condensation-sorting of pancreatic enzymes. ZG16b/PAUF, a paralog of ZG16p, has recently been found to play a role in gene regulation and cancer metastasis. However, the detailed functions of ZG16p and ZG16b remain to be clarified. Here, in order to obtain insights into structure-function relationships, we conducted crystallographic studies of human ZG16p lectin as well as its paralog, ZG16b, and determined their crystal structures at 1.65 and 2.75 Å resolution, respectively. ZG16p has a Jacalin-related β-prism fold, the first to be reported among mammalian lectins. The putative sugar-binding site of ZG16p is occupied by a glycerol molecule, mimicking the mannose bound to Jacalin-related mannose-binding-type plant lectins such as Banlec. ZG16b also has a β-prism fold, but some amino acid residues of the putative sugar-binding site differ from those of the mannose-type binding site suggesting altered preference. A positively charged patch, which may bind sulfated groups of the glycosaminoglycans, is located around the putative sugar-binding site of ZG16p and ZG16b. Taken together, we suggest that the sugar-binding site and the adjacent basic patch of ZG16p and ZG16b cooperatively form a functional glycosaminoglycan-binding site.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Glycobiology Team, Systems Glycobiology Research Group, Chemical Biology Department, RIKEN Advanced Science Institute, 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako, Saitama 351-0198, Japan.