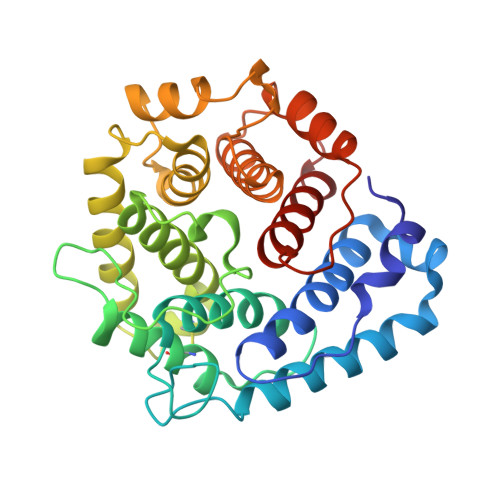
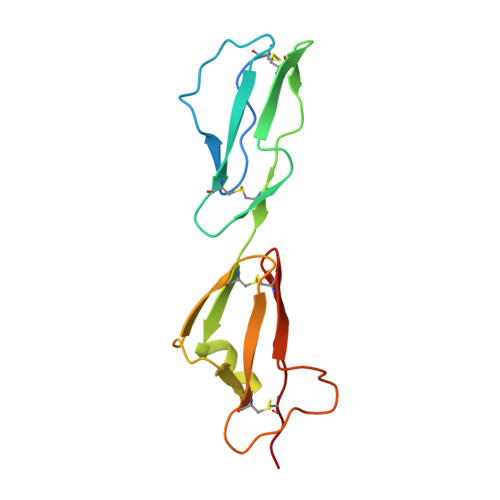
Dual Interaction of Factor H with C3D and Glycosaminoglycans in Host-Nonhost Discrimination by Complement.
Kajander, T., Lehtinen, M.J., Hyvarinen, S., Bhattacharjee, A., Leung, E., Isenman, D.E., Meri, S., Goldman, A., Jokiranta, T.S.(2011) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108: 2897
- PubMed: 21285368
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1017087108
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2XQW - PubMed Abstract:
The alternative pathway of complement is important in innate immunity, attacking not only microbes but all unprotected biological surfaces through powerful amplification. It is unresolved how host and nonhost surfaces are distinguished at the molecular level, but key components are domains 19-20 of the complement regulator factor H (FH), which interact with host (i.e., nonactivator surface glycosaminoglycans or sialic acids) and the C3d part of C3b. Our structure of the FH19-20:C3d complex at 2.3-Å resolution shows that FH19-20 has two distinct binding sites, FH19 and FH20, for C3b. We show simultaneous binding of FH19 to C3b and FH20 to nonactivator surface glycosaminoglycans, and we show that both of these interactions are necessary for full binding of FH to C3b on nonactivator surfaces (i.e., for target discrimination). We also show that C3d could replace glycosaminoglycan binding to FH20, thus providing a feedback control for preventing excess C3b deposition and complement amplification. This explains the molecular basis of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome, where mutations on the binding interfaces between FH19-20 and C3d or between FH20 and glycosaminoglycans lead to complement attack against host surfaces.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Biotechnology, University of Helsinki, Viikinkaari, FIN-00014, Helsinki, Finland.