A novel inhibitor of the alternative pathway of complement reverses inflammation and bone destruction in experimental arthritis.
Katschke, K.J., Helmy, K.Y., Steffek, M., Xi, H., Yin, J., Lee, W.P., Gribling, P., Barck, K.H., Carano, R.A., Taylor, R.E., Rangell, L., Diehl, L., Hass, P.E., Wiesmann, C., van Lookerenb Campagne, M.(2007) J Exp Med 204: 1319-1325
- PubMed: 17548523
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20070432
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
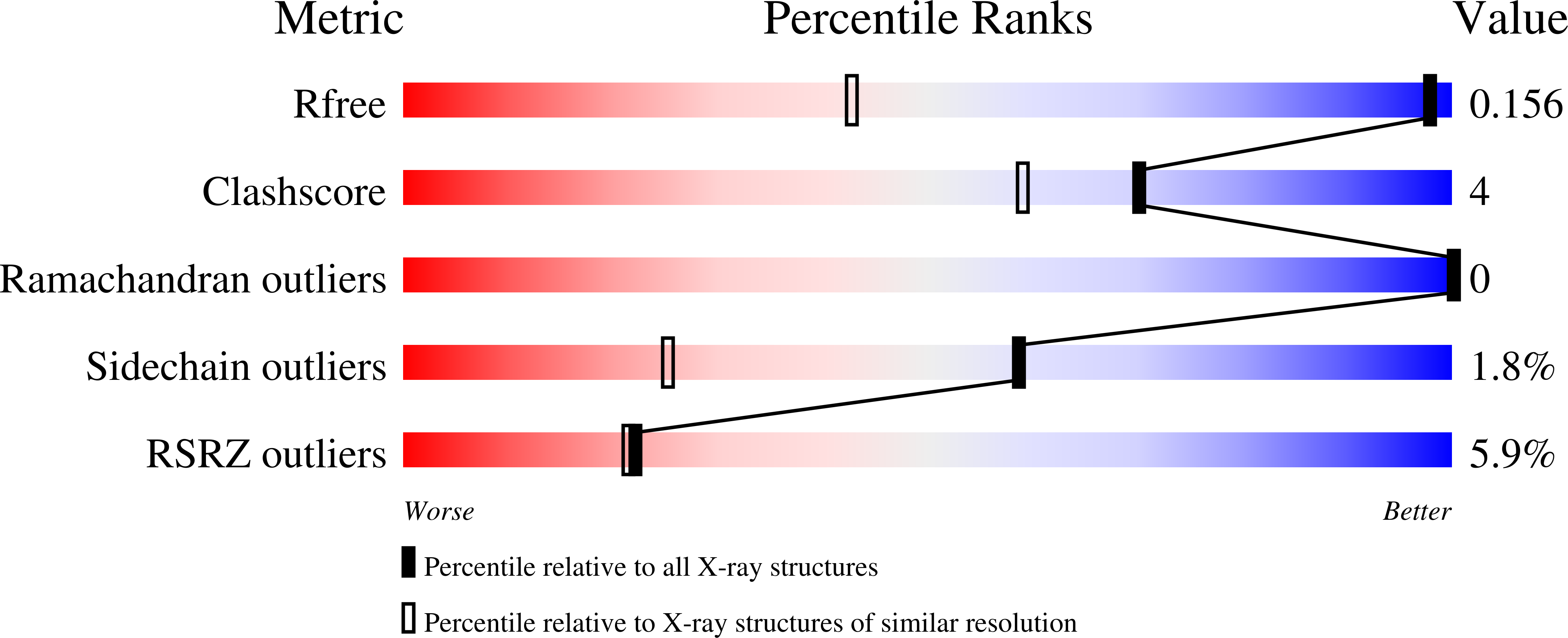
2PND - PubMed Abstract:
Complement is an important component of the innate and adaptive immune response, yet complement split products generated through activation of each of the three complement pathways (classical, alternative, and lectin) can cause inflammation and tissue destruction. Previous studies have shown that complement activation through the alternative, but not classical, pathway is required to initiate antibody-induced arthritis in mice, but it is unclear if the alternative pathway (AP) plays a role in established disease. Previously, we have shown that human complement receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily (CRIg) is a selective inhibitor of the AP of complement. Here, we present the crystal structure of murine CRIg and, using mutants, provide evidence that the structural requirements for inhibition of the AP are conserved in human and mouse. A soluble form of CRIg reversed inflammation and bone loss in two experimental models of arthritis by inhibiting the AP of complement in the joint. Our data indicate that the AP of complement is not only required for disease induction, but also disease progression. The extracellular domain of CRIg thus provides a novel tool to study the effects of inhibiting the AP of complement in established disease and constitutes a promising therapeutic with selectivity for a single complement pathway.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Immunology, Genentech, Inc., San Francisco, CA 94080, USA.