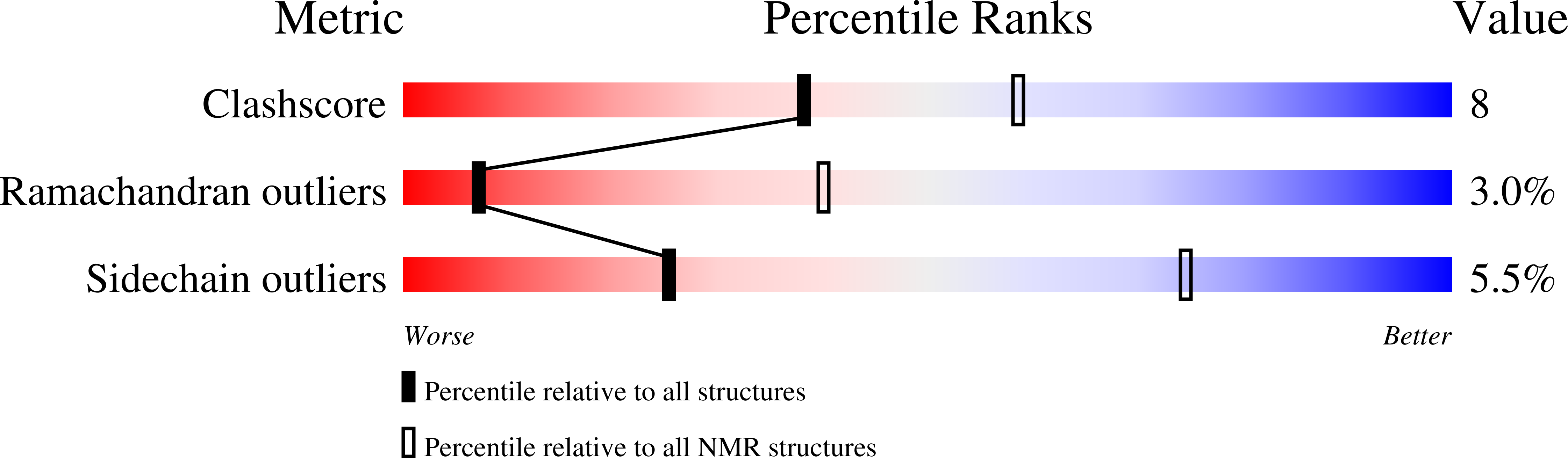
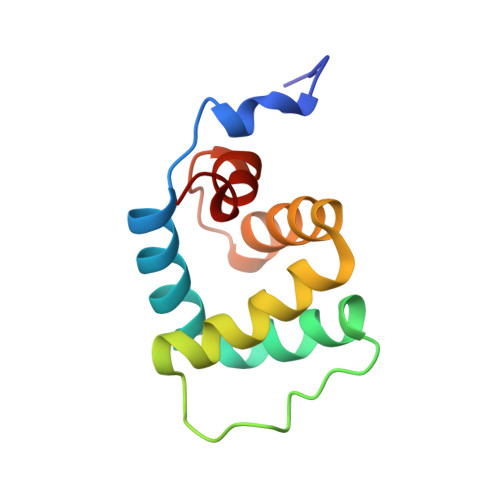
Unusual structural features revealed by the solution NMR structure of the NLRC5 caspase recruitment domain.
Gutte, P.G., Jurt, S., Grutter, M.G., Zerbe, O.(2014) Biochemistry 53: 3106-3117
- PubMed: 24815518
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi500177x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2MJM - PubMed Abstract:
The cytosolic nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat-containing receptors (NLRs) are key sensors for bacterial and viral invaders and endogenous stress signals. NLRs contain a varying N-terminal effector domain that regulates the downstream signaling events upon its activation and determines the subclass to which a NLR member belongs. NLRC5 contains an unclassified N-terminal effector domain that has been reported to interact downstream with the tandem caspase recruitment domain (CARD) of retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I). Here we report the solution structure of the N-terminal effector domain of NLRC5 and in vitro interaction experiments with the tandem CARD of RIG-I. The N-terminal effector domain of NLRC5 adopts a six α-helix bundle with a general death fold, though it displays specific structural features that are strikingly different from the CARD. Notably, α-helix 3 is replaced by an ordered loop, and α-helix 1 is devoid of the characteristic interruption. Detailed structural alignments between the N-terminal effector domains of NLRC5 with a representative of each death-fold subfamily showed that NLRC5 fits best to the CARD subfamily and can be called an atypical CARD. Due to the specific structural features, the atypical CARD also displays a different electrostatic surface. Because the shape and charge of the surface is crucial for the establishment of a homotypic CARD-CARD interaction, these specific structural features seem to have a significant effect on the interaction between the atypical CARD of NLRC5 and the tandem RIG-I CARD.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Biochemistry, University of Zurich , Winterthurerstrasse 190, CH-8057 Zurich, Switzerland.