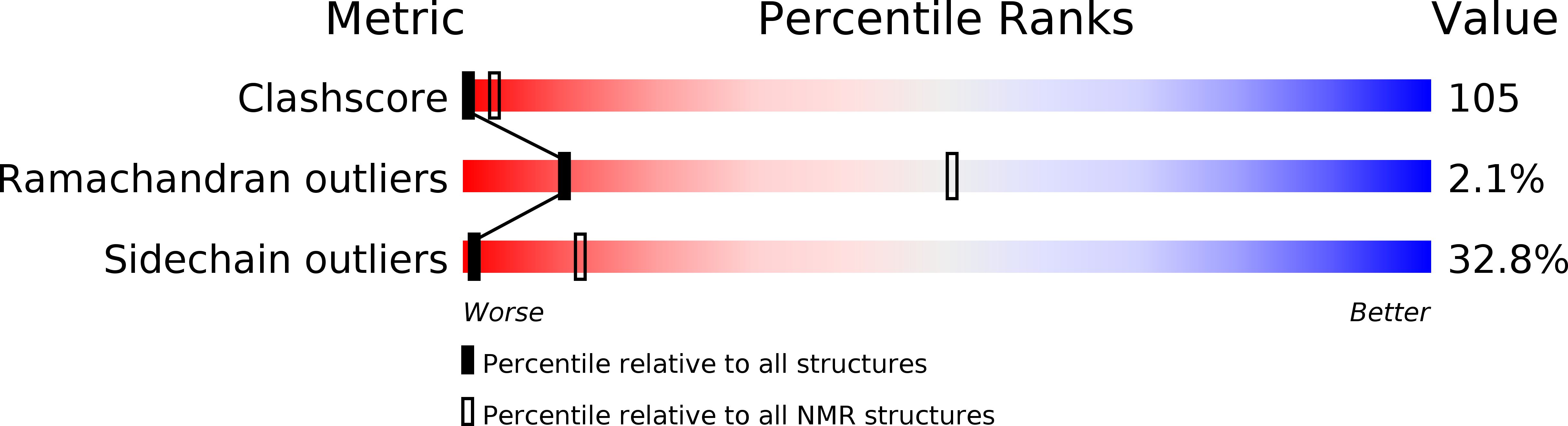The design involved in PapI and Lrp regulation of the pap operon.
Kawamura, T., Vartanian, A.S., Zhou, H., Dahlquist, F.W.(2011) J Mol Biol 409: 311-332
- PubMed: 21338611
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2011.01.058
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2L4A - PubMed Abstract:
The uropathogenic Escherichia coli colonize the host body by attaching themselves to the epithelial cells through the pyelonephritis-associated pili (pap). The expression of the papBA operon is regulated under a reversible phase-variation mechanism, which partitions the population of cells into those that express the pap and others that do not. The two phases of pap expression are the direct consequences of the two distinct DNA-binding modes exhibited by leucine-responsive regulatory protein (Lrp) in the pap promoter region. In the phase-OFF cells, Lrp occupies the binding sites proximal to the transcription start, blocking transcription initiation. In the phase-ON cells, Lrp occupies the binding sites distal to the transcription start and is thought to promote the CAP (catabolite gene activation protein)-directed transcription initiation. Lrp binds to the proximal binding sites more tightly than to the distal sites, and the switching from phase-OFF to phase-ON requires a local co-regulator, PapI. Here, we used PapI and an isolated DNA-binding domain construct of Lrp to show that there is a DNA co-recognition mechanism by which both proteins acquire enhanced affinity to the distal pap site DNA, to which neither of them binds to an appreciable extent without the other. Also, examination of the binding properties of the Lrp DNA-binding domain presented here led us to propose a new sequence alignment of the six pap Lrp-binding sites. New insights into the design of sequences regulating the pap phase variation as revealed by the pap Lrp-binding site sequences are thus defined and discussed.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of California, Santa Barbara, USA.