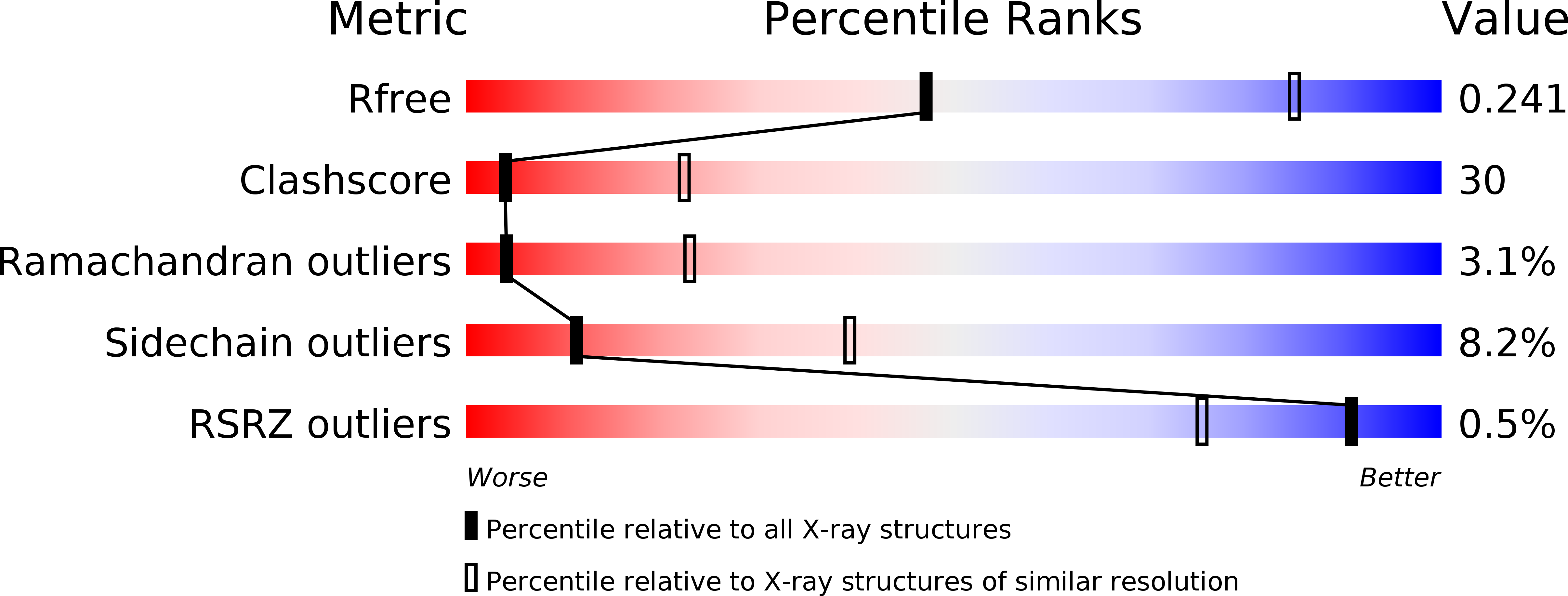
Molecular Structure of a Novel Membrane Protease Specific for a Stomatin Homolog from the Hyperthermophilic Archaeon Pyrococcus horikoshii
Yokoyama, H., Matsui, E., Akiba, T., Harata, K., Matsui, I.(2006) J Mol Biol 358: 1152-1164
- PubMed: 16574150
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2006.02.052
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2DEO - PubMed Abstract:
Membrane-bound proteases are involved in various regulatory functions. Our previous study indicated that the N-terminal region of an open reading frame, PH1510 (residues 16-236, designated as 1510-N) from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus horikoshii, is a serine protease with a catalytic Ser-Lys dyad that specifically cleaves the C-terminal hydrophobic residues of a membrane protein, the stomatin-homolog PH1511. In humans, an absence of stomatin is associated with a form of hemolytic anemia known as hereditary stomatocytosis, but the function of stomatin is not fully understood. Here, we report the crystal structure of 1510-N in dimeric form. Each active site of 1510-N is rich in hydrophobic residues, which accounts for the substrate-specificity. The monomer of 1510-N shows structural similarity to one monomer of Escherichia coli ClpP, an ATP-dependent tetradecameric protease. But, their oligomeric forms are different. Major contributors to dimeric interaction in 1510-N are the alpha7 helix and beta9 strand, both of which are missing from ClpP. While the long handle region of ClpP contributes to the stacking of two heptameric rings, the corresponding L2 loop of 1510-N is disordered because the region has little interaction with other residues of the same molecule. The catalytic Ser97 of 1510-N is in almost the same location as the catalytic Ser97 of E.coli ClpP, whereas another residue, Lys138, presumably forming the catalytic dyad, is located in the disordered L2 region of 1510-N. These findings suggest that the binding of the substrate to the catalytic site of 1510-N induces conformational changes in a region that includes loop L2 so that Lys138 approaches the catalytic Ser97.
Organizational Affiliation:
Biological Information Research Center, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8566, Japan.