Kinetic, Inhibition and Structural Studies on 3-Oxoacyl-Acp Reductase from Plasmodium Falciparum, a Key Enzyme in Fatty Acid Biosynthesis.
Wickramasinghe, S.R., Inglis, K.A., Urch, J.E., Muller, S., Van Aalten, D.M.F., Fairlamb, A.H.(2006) Biochem J 393: 447
- PubMed: 16225460
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20050832
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2C07 - PubMed Abstract:
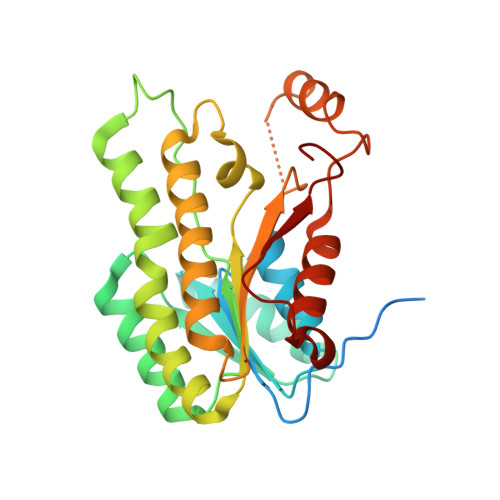
Type II fatty acid biosynthesis represents an attractive target for the discovery of new antimalarial drugs. Previous studies have identified malarial ENR (enoyl acyl-carrier-protein reductase, or FabI) as the target for the antiseptic triclosan. In the present paper, we report the biochemical properties and 1.5 A (1 A=0.1 nm) crystal structure of OAR (3-oxoacyl acyl-carrier-protein reductase, or FabG), the second reductive step in fatty acid biosynthesis and its inhibition by hexachlorophene. Under optimal conditions of pH and ionic strength, Plasmodium falciparum OAR displays kinetic properties similar to those of OAR from bacteria or plants. Activity with NADH is <3% of that with NADPH. Fluorescence enhancement studies indicate that NADPH can bind to the free enzyme, consistent with kinetic and product inhibition studies suggesting a steady-state ordered mechanism. The crystal structure reveals a tetramer with a sulphate ion bound in the cofactor-binding site such that the side chains of the catalytic triad of serine, tyrosine and lysine are aligned in an active conformation, as previously observed in the Escherichia coli OAR-NADP+ complex. A cluster of positively charged residues is positioned at the entrance to the active site, consistent with the proposed recognition site for the physiological substrate (3-oxoacyl-acyl-carrier protein) in E. coli OAR. The antibacterial and anthelminthic agent hexachlorophene is a potent inhibitor of OAR (IC50 2.05 microM) displaying non-linear competitive inhibition with respect to NADPH. Hexachlorophene (EC50 6.2 microM) and analogues such as bithionol also have antimalarial activity in vitro, suggesting they might be useful leads for further development.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Biological Chemistry and Molecular Microbiology, School of Life Sciences, University of Dundee, Dundee DD1 5EH, UK.