Structure and Reactivity of Hydroxypropylphosphonic Acid Epoxidase in Fosfomycin Biosynthesis by a Cation- and Flavin-Dependent Mechanism.
Mcluskey, K., Cameron, S., Hammerschmidt, F., Hunter, W.N.(2005) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102: 14221
- PubMed: 16186494
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0504314102
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
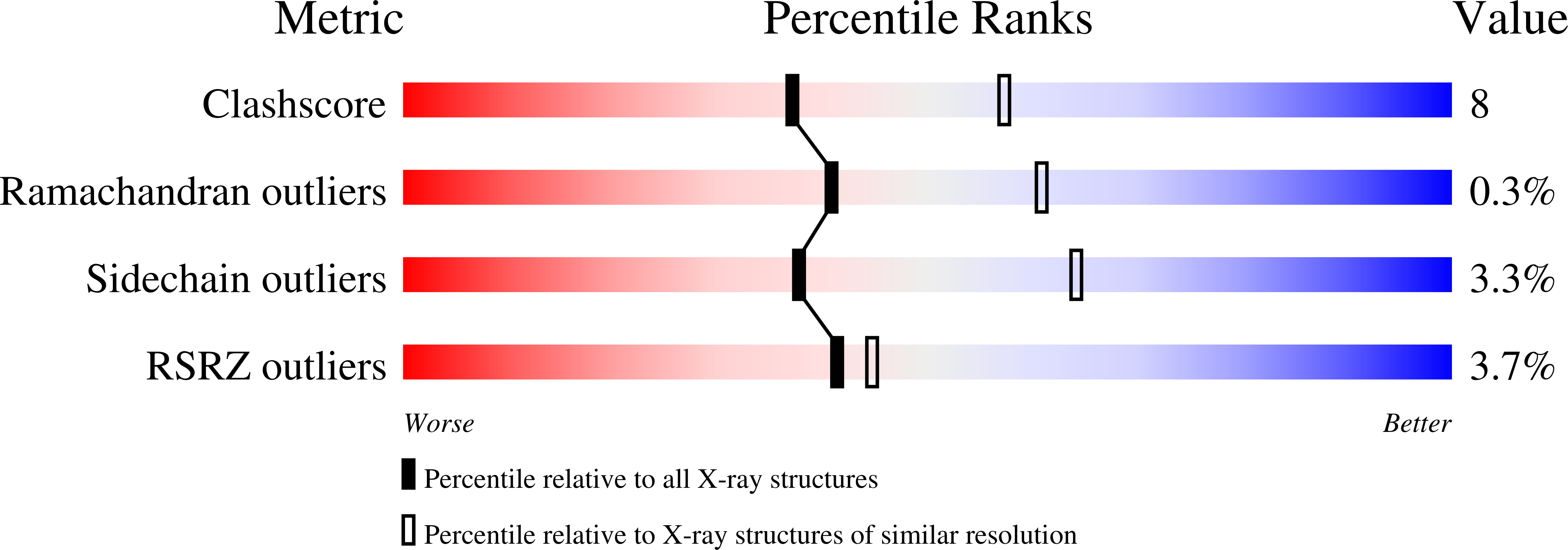
2BNM, 2BNN, 2BNO - PubMed Abstract:
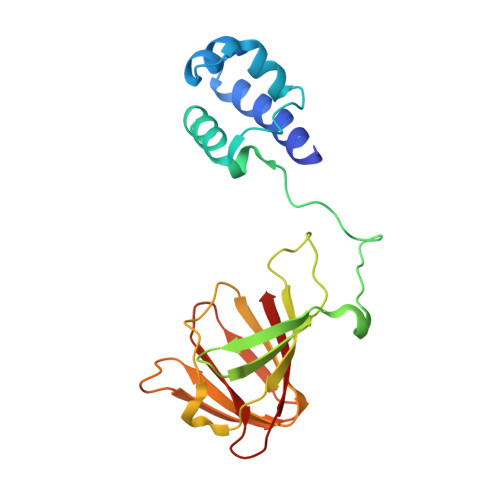
The biosynthesis of fosfomycin, an oxirane antibiotic in clinical use, involves a unique epoxidation catalyzed by (S)-2-hydroxypropylphosphonic acid epoxidase (HPPE). The reaction is essentially dehydrogenation of a secondary alcohol. A high-resolution crystallographic analysis reveals that the HPPE subunit displays a two-domain combination. The C-terminal or catalytic domain has the cupin fold that binds a divalent cation, whereas the N-terminal domain carries a helix-turn-helix motif with putative DNA-binding helices positioned 34 A apart. The structure of HPPE serves as a model for numerous proteins, of ill-defined function, predicted to be transcription factors but carrying a cupin domain at the C terminus. Structure-reactivity analyses reveal conformational changes near the catalytic center driven by the presence or absence of ligand, that HPPE is a Zn(2+)/Fe(2+)-dependent epoxidase, proof that flavin mononucleotide is required for catalysis, and allow us to propose a simple mechanism that is compatible with previous experimental data. The participation of the redox inert Zn(2+) in the mechanism is surprising and indicates that Lewis acid properties of the metal ions are sufficient to polarize the substrate and, aided by flavin mononucleotide reduction, facilitate the epoxidation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Biological Chemistry and Molecular Microbiology, School of Life Sciences, University of Dundee, Dundee DD1 5EH, United Kingdom.