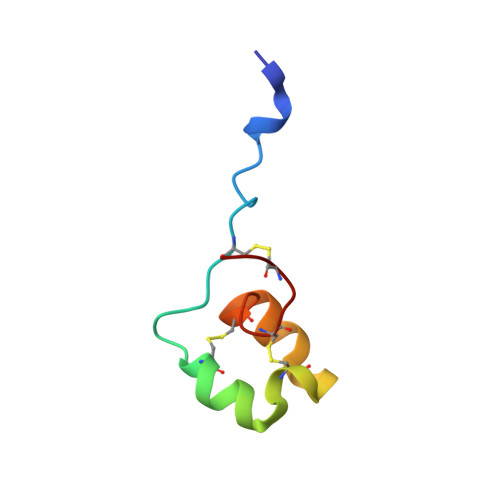
Kv1.3 channel-blocking immunomodulatory peptides from parasitic worms: implications for autoimmune diseases.
Chhabra, S., Chang, S.C., Nguyen, H.M., Huq, R., Tanner, M.R., Londono, L.M., Estrada, R., Dhawan, V., Chauhan, S., Upadhyay, S.K., Gindin, M., Hotez, P.J., Valenzuela, J.G., Mohanty, B., Swarbrick, J.D., Wulff, H., Iadonato, S.P., Gutman, G.A., Beeton, C., Pennington, M.W., Norton, R.S., Chandy, K.G.(2014) FASEB J 28: 3952-3964
- PubMed: 24891519
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.14-251967
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2MCR, 2MD0 - PubMed Abstract:
The voltage-gated potassium (Kv) 1.3 channel is widely regarded as a therapeutic target for immunomodulation in autoimmune diseases. ShK-186, a selective inhibitor of Kv1.3 channels, ameliorates autoimmune diseases in rodent models, and human phase 1 trials of this agent in healthy volunteers have been completed. In this study, we identified and characterized a large family of Stichodactyla helianthus toxin (ShK)-related peptides in parasitic worms. Based on phylogenetic analysis, 2 worm peptides were selected for study: AcK1, a 51-residue peptide expressed in the anterior secretory glands of the dog-infecting hookworm Ancylostoma caninum and the human-infecting hookworm Ancylostoma ceylanicum, and BmK1, the C-terminal domain of a metalloprotease from the filarial worm Brugia malayi. These peptides in solution adopt helical structures closely resembling that of ShK. At doses in the nanomolar-micromolar range, they block native Kv1.3 in human T cells and cloned Kv1.3 stably expressed in L929 mouse fibroblasts. They preferentially suppress the proliferation of rat CCR7(-) effector memory T cells without affecting naive and central memory subsets and inhibit the delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) response caused by skin-homing effector memory T cells in rats. Further, they suppress IFNγ production by human T lymphocytes. ShK-related peptides in parasitic worms may contribute to the potential beneficial effects of probiotic parasitic worm therapy in human autoimmune diseases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Medicinal Chemistry, Monash Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Monash University, Parkville, Victoria, Australia;