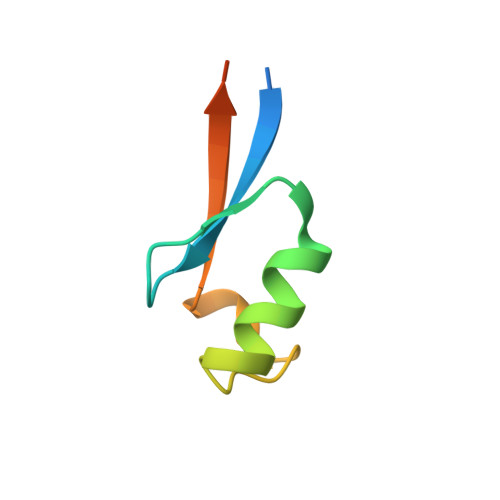
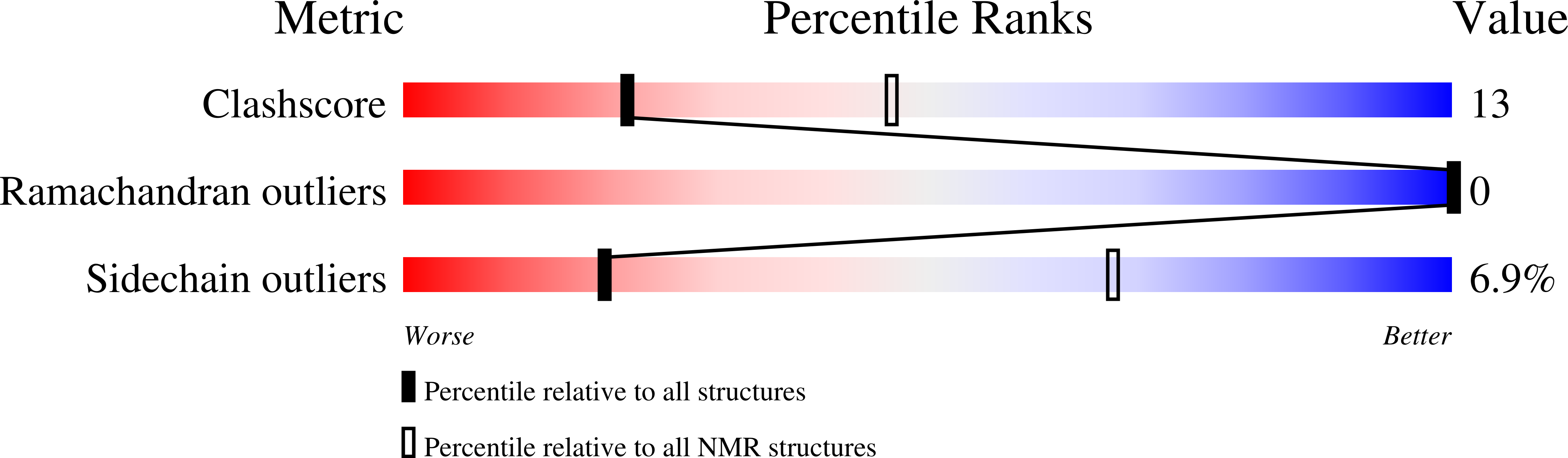Solution structure of an archaeal DNA binding protein with an eukaryotic zinc finger fold.
Guilliere, F., Danioux, C., Jaubert, C., Desnoues, N., Delepierre, M., Prangishvili, D., Sezonov, G., Guijarro, J.I.(2013) PLoS One 8: e52908-e52908
- PubMed: 23326363
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0052908
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2LVH - PubMed Abstract:
While the basal transcription machinery in archaea is eukaryal-like, transcription factors in archaea and their viruses are usually related to bacterial transcription factors. Nevertheless, some of these organisms show predicted classical zinc fingers motifs of the C2H2 type, which are almost exclusively found in proteins of eukaryotes and most often associated with transcription regulators. In this work, we focused on the protein AFV1p06 from the hyperthermophilic archaeal virus AFV1. The sequence of the protein consists of the classical eukaryotic C2H2 motif with the fourth histidine coordinating zinc missing, as well as of N- and C-terminal extensions. We showed that the protein AFV1p06 binds zinc and solved its solution structure by NMR. AFV1p06 displays a zinc finger fold with a novel structure extension and disordered N- and C-termini. Structure calculations show that a glutamic acid residue that coordinates zinc replaces the fourth histidine of the C2H2 motif. Electromobility gel shift assays indicate that the protein binds to DNA with different affinities depending on the DNA sequence. AFV1p06 is the first experimentally characterised archaeal zinc finger protein with a DNA binding activity. The AFV1p06 protein family has homologues in diverse viruses of hyperthermophilic archaea. A phylogenetic analysis points out a common origin of archaeal and eukaryotic C2H2 zinc fingers.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institut Pasteur, Unité de RMN des Biomolécules, Département de Biologie Structurale et Chimie, Paris, France.