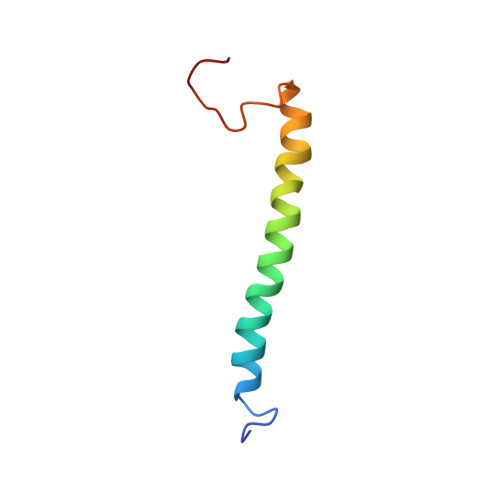
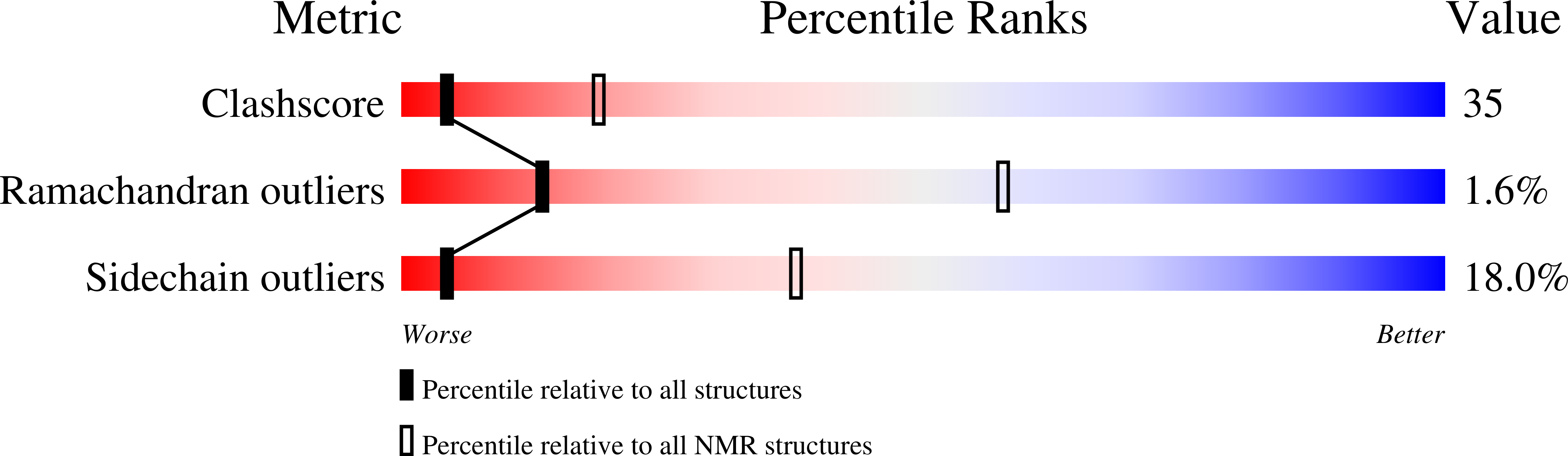Solution Structures of the Core Light-harvesting alpha and beta Polypeptides from Rhodospirillum rubrum: Implications for the Pigment-Protein and Protein-Protein Interactions
Wang, Z.-Y., Gokan, K., Kobayashi, M., Nozawa, T.(2005) J Mol Biol 347: 465-477
- PubMed: 15740753
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2005.01.017
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1WRG, 1XRD - PubMed Abstract:
We have determined the solution structures of the core light-harvesting (LH1) alpha and beta-polypeptides from wild-type purple photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum using multidimensional NMR spectroscopy. The two polypeptides form stable alpha helices in organic solution. The structure of alpha-polypeptide consists of a long helix of 32 amino acid residues over the central transmembrane domain and a short helical segment at the N terminus that is followed by a three-residue loop. Pigment-coordinating histidine residue (His29) in the alpha-polypeptide is located near the middle of the central helix. The structure of beta-polypeptide shows a single helix of 32 amino acid residues in the membrane-spanning region with the pigment-coordinating histidine residue (His38) at a position close to the C-terminal end of the helix. Strong hydrogen bonds have been identified for the backbone amide protons over the central helical regions, indicating a rigid property of the two polypeptides. The overall structures of the R.rubrum LH1 alpha and beta-polypeptides are different from those previously reported for the LH1 beta-polypeptide of Rhodobacter sphaeroides, but are very similar to the structures of the corresponding LH2 alpha and beta-polypeptides determined by X-ray crystallography. A model constructed for the structural subunit (B820) of LH1 complex using the solution structures reveals several important features on the interactions between the LH1 alpha and beta-polypeptides. The significance of the N-terminal regions of the two polypeptides for stabilizing both B820 and LH1 complexes, as clarified by many experiments, may be attributed to the interactions between the short N-terminal helix (Trp2-Gln6) of alpha-polypeptide and a GxxxG motif in the beta-polypeptide.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biomolecular Engineering, Graduate School of Engineering, Tohoku University, Aramaki-aza, Aoba, Aoba-ku, Sendai 980-8579, Japan. wang@biophys.che.tohoku.ac.jp