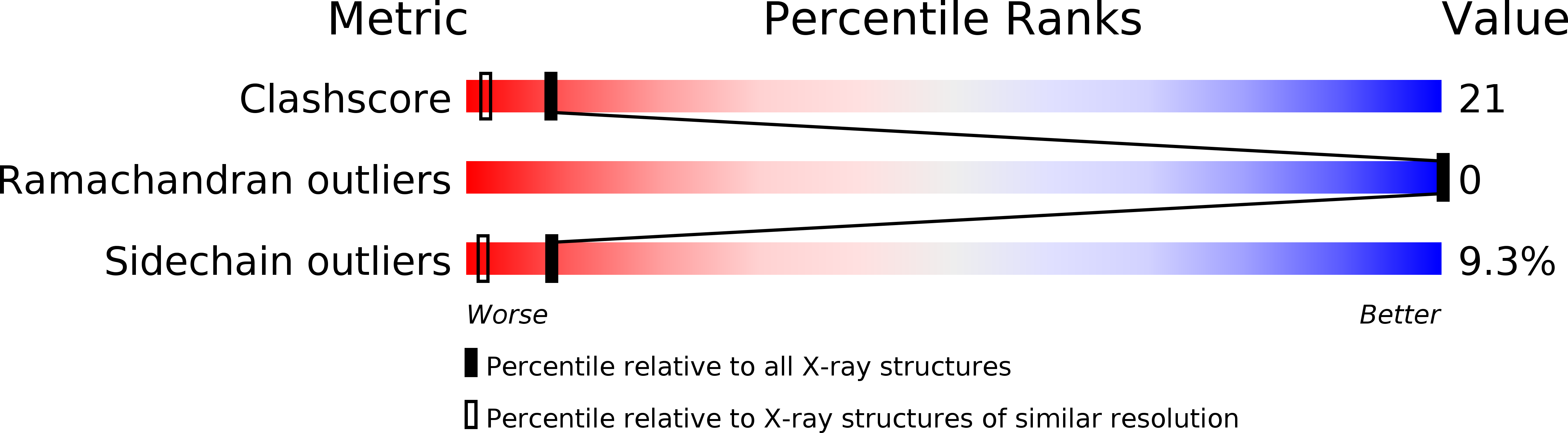Crystal structures of two alpha-like scorpion toxins: non-proline cis peptide bonds and implications for new binding site selectivity on the sodium channel.
He, X.L., Li, H.M., Zeng, Z.H., Liu, X.Q., Wang, M., Wang, D.C.(1999) J Mol Biol 292: 125-135
- PubMed: 10493862
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1999.3036
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1SN1, 1SN4 - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structures of two group III alpha-like toxins from the scorpion Buthus martensii Karsch, BmK M1 and BmK M4, were determined at 1.7 A and 1.3 A resolution and refined to R factors of 0.169 and 0.166, respectively. The first high-resolution structures of the alpha-like scorpion toxin show some striking features compared with structures of the "classical" alpha-toxin. Firstly, a non-proline cis peptide bond between residues 9 and 10 unusually occurs in the five-member reverse turn 8-12. Secondly, the cis peptide 9-10 mediates the spatial relationship between the turn 8-12 and the C-terminal stretch 58-64 through a pair of main-chain hydrogen bonds between residues 10 and 64 to form a unique tertiary arrangement which features the special orientation of the terminal residues 62-64. Finally, in consequence of the peculiar orientation of the C-terminal residues, the functional groups of Arg58, which are crucial for the toxin-receptor interaction, are exposed and accessible in BmK M1 and M4 rather than buried as in the classical alpha-toxins. Sequence alignment and characteristics analysis suggested that the above structural features observed in BmK M1 and M4 occur in all group III alpha-like toxins. Recently, some group III alpha-like toxins were demonstrated to occupy a receptor site different from the classical alpha-toxin. Therefore, the distinct structural features of BmK M1 and M4 presented here may provide the structural basis for the newly recognized toxin-receptor binding site selectivity. Besides, the non-proline cis peptide bonds found in these two structures play a role in the formation of the structural characteristics and in keeping accurate positions of the functionally crucial residues. This manifested a way to achieve high levels of molecular specificity and atomic precision through the strained backbone geometry.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100101, P.R. China.