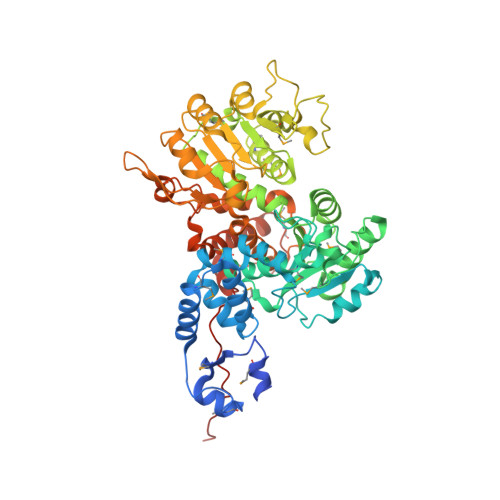
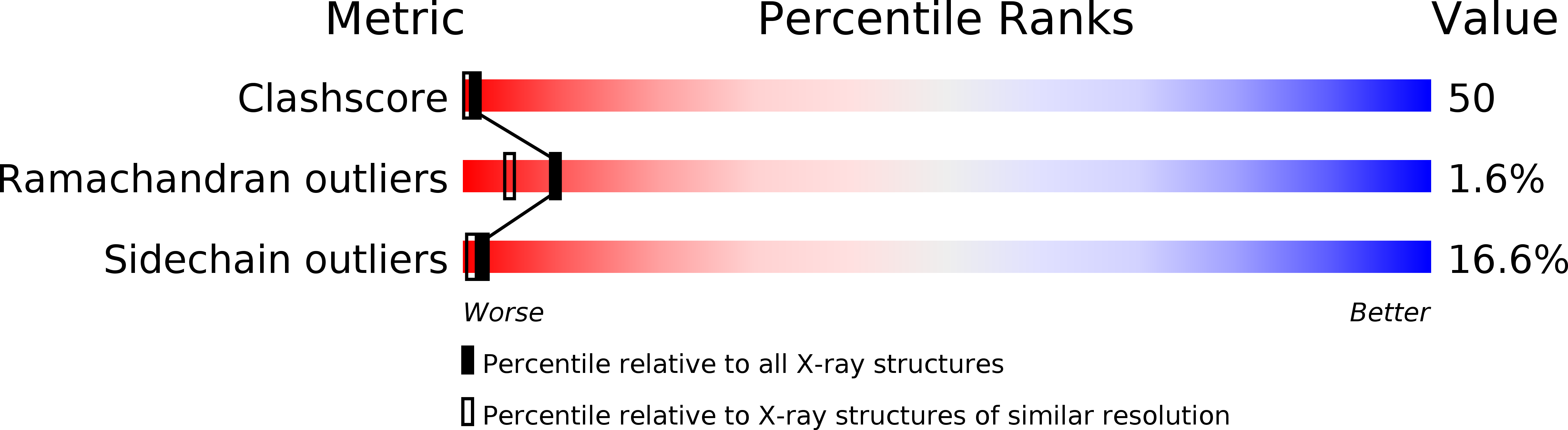Crystal structure of human mitochondrial NAD(P)(+)-dependent malic enzyme: a new class of oxidative decarboxylases.
Xu, Y., Bhargava, G., Wu, H., Loeber, G., Tong, L.(1999) Structure 7: 877-889
- PubMed: 10467136
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1QR6 - PubMed Abstract:
Background: Malic enzymes catalyze the oxidative decarboxylation of malate to pyruvate and CO(2) with the concomitant reduction of NAD(P)(+) to NAD(P)H. They are widely distributed in nature and have important biological functions. Human mitochondrial NAD(P)(+)-dependent malic enzyme (mNAD-ME) may have a crucial role in the metabolism of glutamine for energy production in rapidly dividing cells and tumors. Moreover, this isoform is unique among malic enzymes in that it is a cooperative enzyme, and its activity is controlled allosterically. Results: The crystal structure of human mNAD-ME has been determined at 2.5 Å resolution by the selenomethionyl multiwavelength anomalous diffraction method and refined to 2.1 Å resolution. The structure of the monomer can be divided into four domains; the active site of the enzyme is located in a deep cleft at the interface between three of the domains. Three acidic residues (Glu255, Asp256 and Asp279) were identified as ligands for the divalent cation that is required for catalysis by malic enzymes. Conclusions: The structure reveals that malic enzymes belong to a new class of oxidative decarboxylases. The tetramer of the enzyme appears to be a dimer of dimers. The active site of each monomer is located far from the tetramer interface. The structure also shows the binding of a second NAD(+) molecule in a pocket 35 Å away from the active site. The natural ligand for this second binding site may be ATP, an allosteric inhibitor of the enzyme.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences Columbia University New York, NY 10027, USA