Crystal Structure of Actinomycin D Bound to the Ctg Triplet Repeat Sequences Linked to Neurological Diseases
Hou, M.-H., Robinson, H., Gao, Y.-G., Wang, A.H.-J.(2002) Nucleic Acids Res 30: 4910
- PubMed: 12433994
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkf619
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
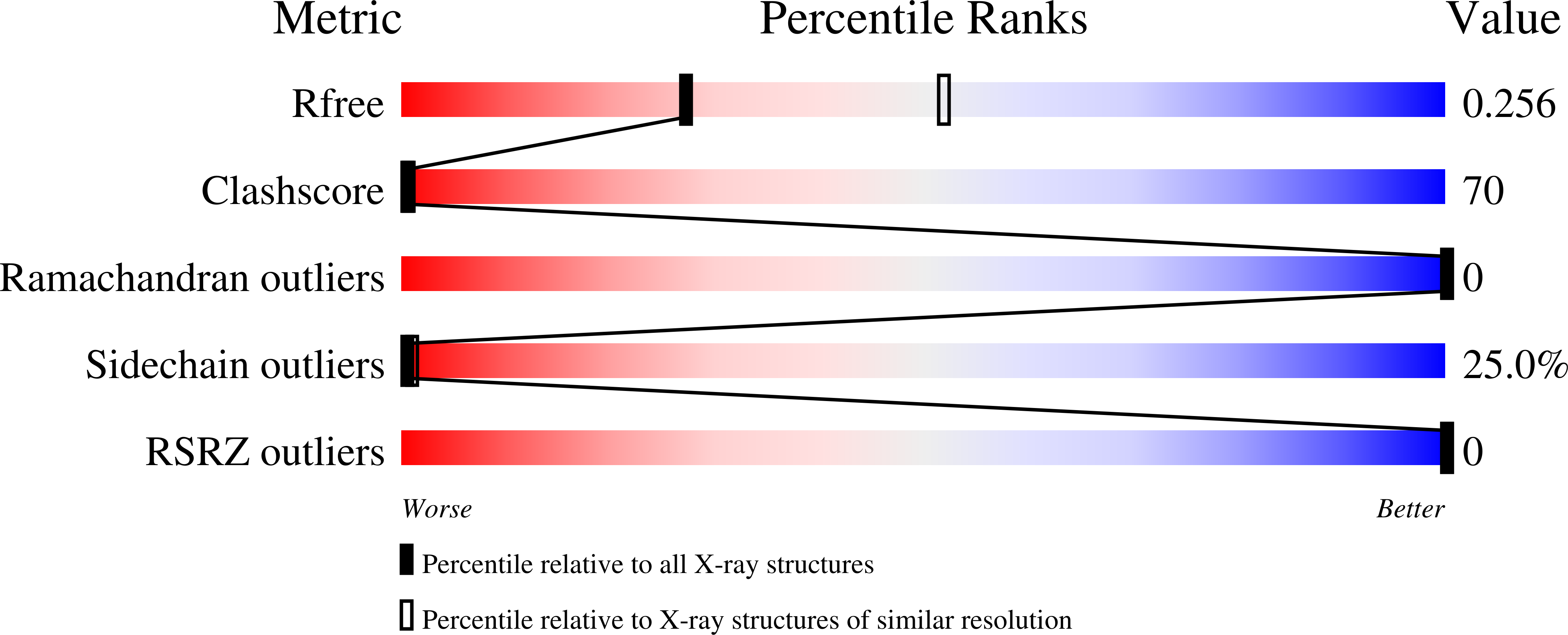
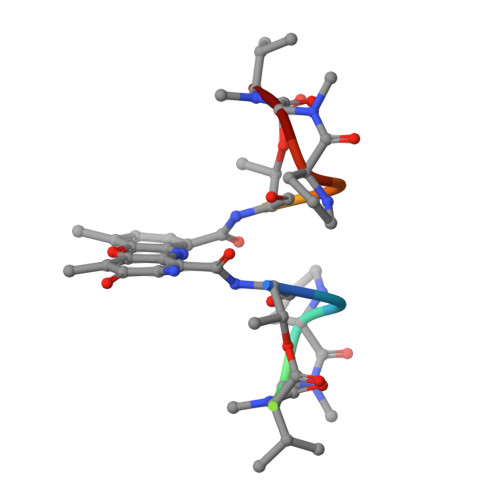
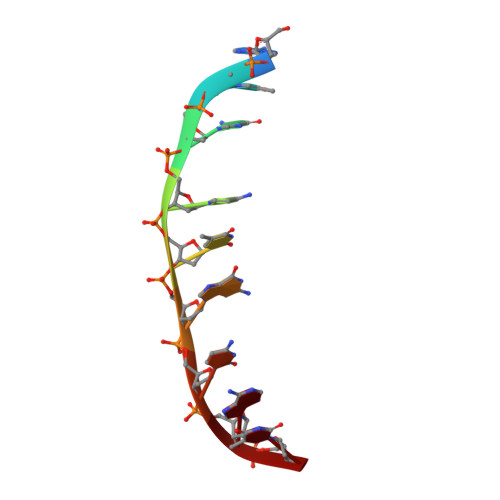
1MNV - PubMed Abstract:
The potent anticancer drug actinomycin D (ActD) acts by binding to DNA GpC sequences, thereby interfering with essential biological processes including replication, transcription and topoisomerase. Certain neurological diseases are correlated with expansion of (CTG)n trinucleotide sequences, which contain many contiguous GpC sites separated by a single base pair. In order to characterize the binding of ActD to CTG triplet repeat sequences, we carried out heat denaturation and CD analyses, which showed that adjacent GpC sequences flanking a T:T mismatch are preferred ActD-binding sites, and that ActD binding results in a conformational transition to A-type structure. The structural basis of the strong binding of ActD to neighboring GpC sites flanking a T:T mismatch was provided by the crystal structure of ActD bound to ATGCTGCAT, which contains a CTG triplet sequence. Binding of two ActD molecules to GCTGC causes a kink in the DNA helix. In addition, using a synthetic self-priming DNA model, 5'-(CAG)4(CTG)(16)-3', we observed that ActD can trap the cruciform or duplexes of (CTG)n and interfere with the expansion process of CTG triplet repeats as shown by gel electrophoretic expansion assay. Our results may provide the possible biological consequence of ActD bound to CTG triplet repeat sequences.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Biological Chemistry, Academia Sinica, Taipei, 115 Taiwan.