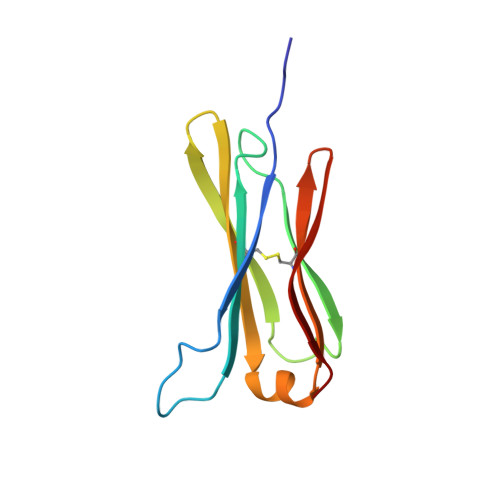
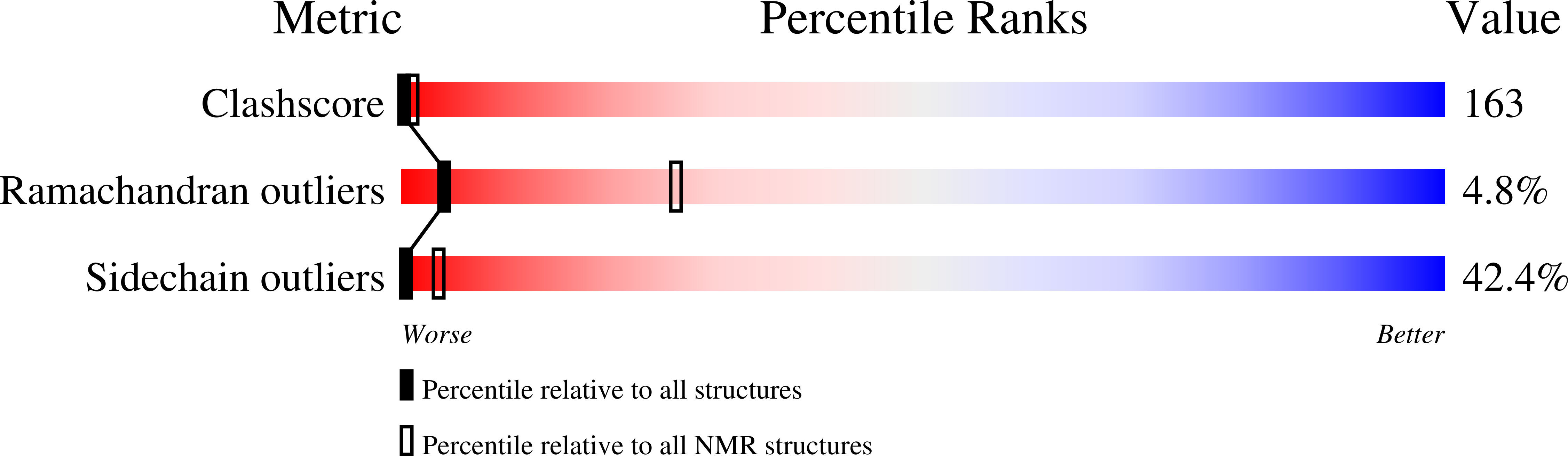The structure of the IgE Cepsilon2 domain and its role in stabilizing the complex with its high-affinity receptor FcepsilonRIalpha.
McDonnell, J.M., Calvert, R., Beavil, R.L., Beavil, A.J., Henry, A.J., Sutton, B.J., Gould, H.J., Cowburn, D.(2001) Nat Struct Biol 8: 437-441
- PubMed: 11323720
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/87603
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1G84 - PubMed Abstract:
The stability of the complex between IgE and its high-affinity receptor, FcepsilonRI, on mast cells is a critical factor in the allergic response. The long half-life of the complex of IgE bound to this receptor in situ ( approximately 2 weeks, compared with only hours for the comparable IgG complex) contributes to the permanent sensitization of these cells and, hence, to the immediate response to allergens. Here we show that the second constant domain of IgE, Cepsilon2, which takes the place of the flexible hinge in IgG, contributes to this long half-life. When the Cepsilon2 domain is deleted from the IgE Fc fragment, leaving only the Cepsilon3 and Cepsilon4 domains (Cepsilon3-4 fragment), the rate of dissociation from the receptor is increased by greater than 1 order of magnitude. We report the structure of the Cepsilon2 domain by heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy and show by chemical shift perturbation that it interacts with FcepsilonRIalpha. By sedimentation equilibrium we show that the Cepsilon2 domain binds to the Cepsilon3-4 fragment of IgE. These interactions of Cepsilon2 with both FcepsilonRIalpha and Cepsilon3-4 provide a structural explanation for the exceptionally slow dissociation of the IgE-FcepsilonRIalpha complex.
Organizational Affiliation:
The Rockefeller University, New York, New York 10021-6399, USA.