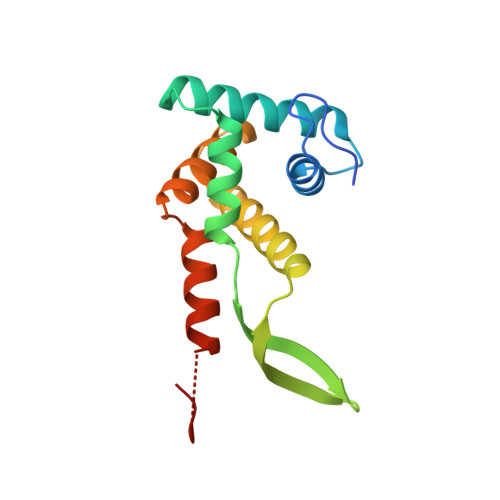
The structure of ribosomal protein S7 at 1.9 A resolution reveals a beta-hairpin motif that binds double-stranded nucleic acids.
Wimberly, B.T., White, S.W., Ramakrishnan, V.(1997) Structure 5: 1187-1198
- PubMed: 9331418
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(97)00269-4
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1RSS - PubMed Abstract:
Ribosomal protein S7, a crucial RNA-binding component of the ribosome, is one of two proteins that initiates assembly of the 30S ribosomal subunit. It is required for proper folding of a large 3' domain of 16S ribosomal RNA. S7 regulates its own synthesis by binding to its own mRNA. This ability of S7 to bind both messenger and ribosomal RNAs makes determination of its mode of RNA recognition particularly interesting. The crystal structure of S7 from Thermus thermophilus was determined by a two-wavelength anomalous diffraction experiment using the LIII edge of mercury. The S7 structure consists of a bundle of six helices and an extended beta hairpin between helices 3 and 4, with two or more RNA-binding sites on its surface. The hairpin, along with portions of helices 1, 4 and 6, forms a large, positively charged, concave surface that has the appropriate curvature and dimensions to bind double-stranded RNA. A second putative RNA-binding site comprises parts of loop 2 and the helix 4-loop 5 turn. Structural similarity between S7 and the IHF/HU family of proteins strongly suggests that the beta hairpin of S7 binds to a groove of double-stranded RNA. The beta hairpin of S7 is also similar to those from other nucleic acid binding proteins, such as ribosomal protein L14 and BIV Tat, suggesting that it belongs to an extended family of such motifs, all of which bind to a groove of double-stranded nucleic acid. The residues in S7 loop 2 that belong to the second putative RNA-binding site may have a role analogous to the N-terminal residues of IHF/HU which grip an unbent portion of double helix.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Utah School of Medicine, Salt Lake City 84132, USA.