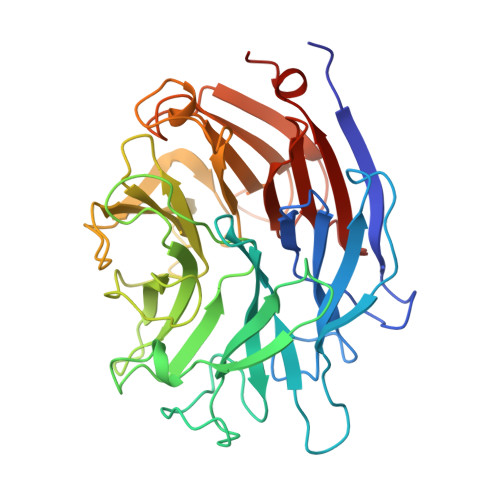
The three domains of a bacterial sialidase: a beta-propeller, an immunoglobulin module and a galactose-binding jelly-roll.
Gaskell, A., Crennell, S., Taylor, G.(1995) Structure 3: 1197-1205
- PubMed: 8591030
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00255-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1EUR, 1EUS, 1EUT, 1EUU - PubMed Abstract:
Sialidases, or neuraminidases, have been implicated in the pathogenesis of many diseases, but are also produced by many non-pathogenic bacteria. Bacterial sialidases are very variable in size, often possessing domains in addition to the catalytic domain. The sialidase from the non-pathogenic soil bacterium Micromonospora viridifaciens is secreted in two forms with molecular weights of 41 kDa or 68 kDa, depending on the nature of the carbohydrate used to induce expression. We report here the X-ray crystal structures of the 41 kDa and 68 kDa forms of the sialidase from M. viridifaciens at 1.8 A and 2.5 A resolution respectively. In addition, we report a complex of the 41 kDa form with an inhibitor at 2.0 A resolution, and a complex of the 68 kDa form with galactose at 2.5 A. The 41 kDa form shows the canonical sialidase beta-propeller fold. The 68 kDa form possesses two additional domains, one with an immunoglobulin-like fold that serves as a linker to the second, which is homologous to the galactose-binding domain of a fungal galactose oxidase. The presence of the additional carbohydrate-binding domain in the 68 kDa form of the bacterial sialidase reported here is a further example of a combination of carbohydrate binding and cleaving domains which we observed in the sialidase from Vibrio cholerae. This dual function may be common, but only to other bacterial and parasitic sialidases, but also to other secreted glycosidases involved in pathogenesis. The bacterium may have acquired both the immunoglobulin module and the galactose-binding module from eukaryotes, as the enzyme shows a remarkable similarity to a fungal galactose oxidase which possesses similar domains performing different functions and assembled in a different order.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Biology and Biochemistry, University of Bath, UK.