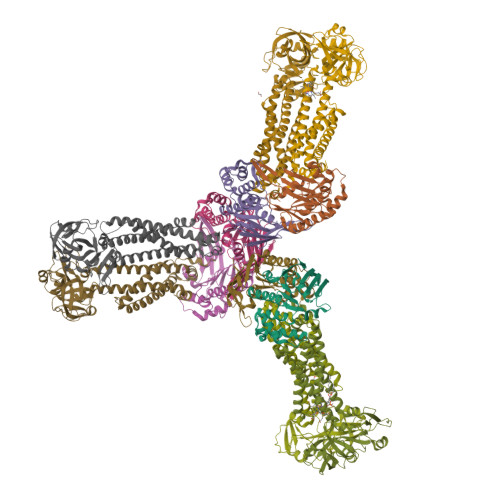
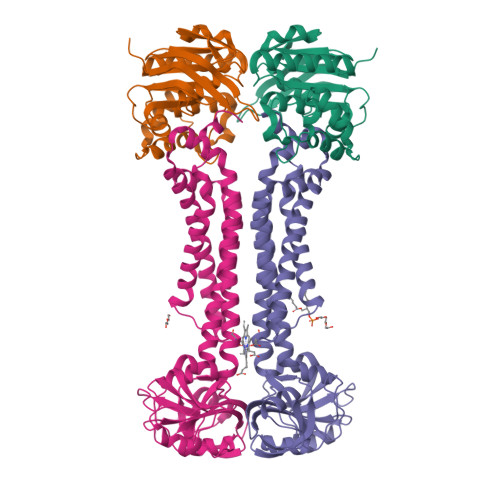
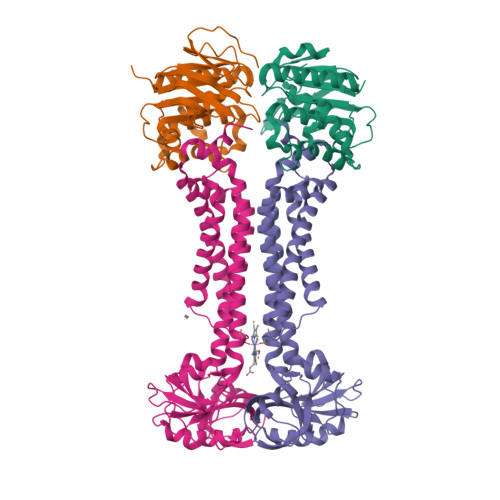
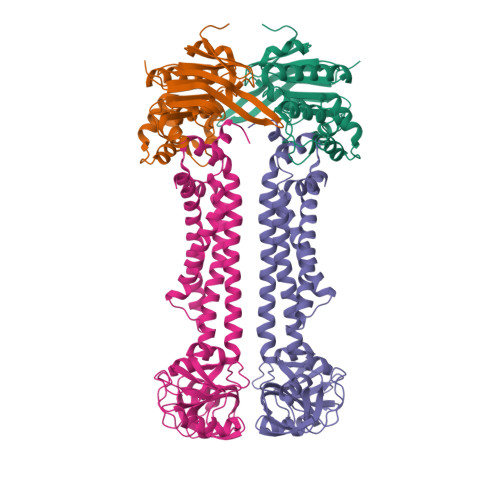
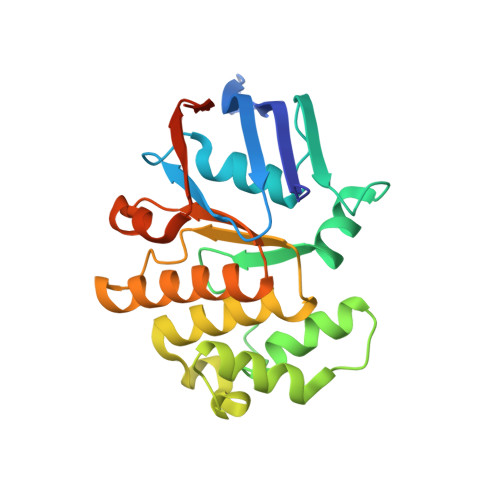
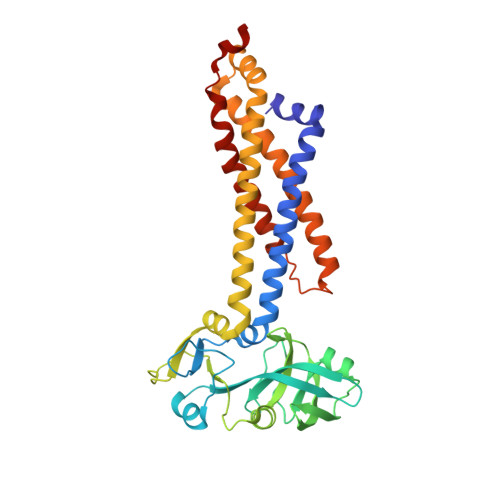
Structural basis for heme detoxification by an ATP-binding cassette-type efflux pump in gram-positive pathogenic bacteria.
Nakamura, H., Hisano, T., Rahman, M.M., Tosha, T., Shirouzu, M., Shiro, Y.(2022) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 119: e2123385119-e2123385119
- PubMed: 35767641
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2123385119
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7W78, 7W79, 7W7A, 7W7B, 7W7C, 7W7D - PubMed Abstract:
Bacterial pathogens acquire heme from the host hemoglobin as an iron nutrient for their virulence and proliferation in blood. Concurrently, they encounter cytotoxic-free heme that escapes the heme-acquisition process. To overcome this toxicity, many gram-positive bacteria employ an ATP-binding cassette heme-dedicated efflux pump, HrtBA in the cytoplasmic membranes. Although genetic analyses have suggested that HrtBA expels heme from the bacterial membranes, the molecular mechanism of heme efflux remains elusive due to the lack of protein studies. Here, we show the biochemical properties and crystal structures of Corynebacterium diphtheriae HrtBA, alone and in complex with heme or an ATP analog, and we reveal how HrtBA extracts heme from the membrane and releases it. HrtBA consists of two cytoplasmic HrtA ATPase subunits and two transmembrane HrtB permease subunits. A heme-binding site is formed in the HrtB dimer and is laterally accessible to heme in the outer leaflet of the membrane. The heme-binding site captures heme from the membrane using a glutamate residue of either subunit as an axial ligand and sequesters the heme within the rearranged transmembrane helix bundle. By ATP-driven HrtA dimerization, the heme-binding site is squeezed to extrude the bound heme. The mechanism sheds light on the detoxification of membrane-bound heme in this bacterium.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory for Protein Functional and Structural Biology, RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics Research, Yokohama 230-0045, Japan.