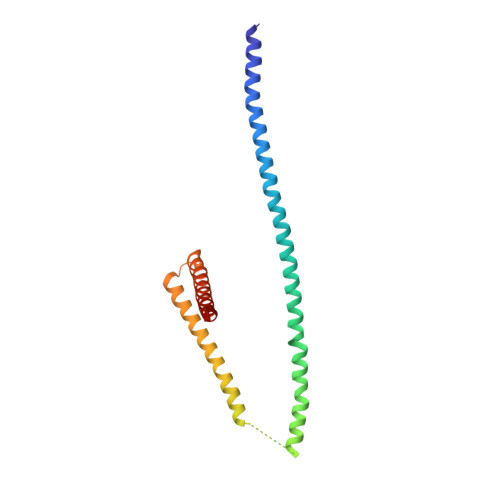
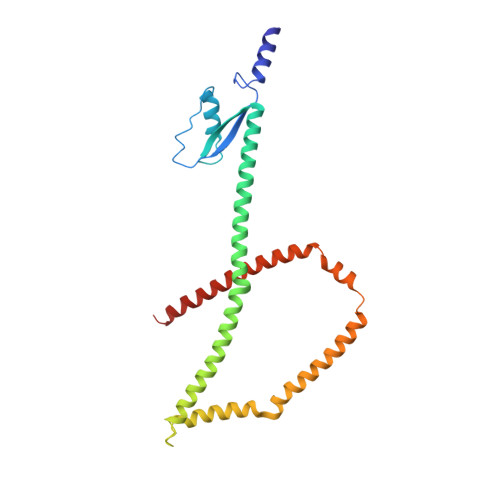
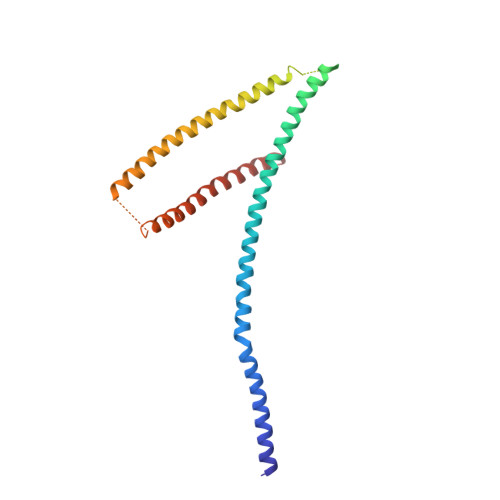Architecture of the linker-scaffold in the nuclear pore.
Petrovic, S., Samanta, D., Perriches, T., Bley, C.J., Thierbach, K., Brown, B., Nie, S., Mobbs, G.W., Stevens, T.A., Liu, X., Tomaleri, G.P., Schaus, L., Hoelz, A.(2022) Science 376: eabm9798-eabm9798
- PubMed: 35679425
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abm9798
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7MVT, 7MVU, 7MVV, 7MVW, 7MVX, 7MVY, 7MVZ, 7MW0, 7MW1, 7TBI, 7TBJ, 7TBK - PubMed Abstract:
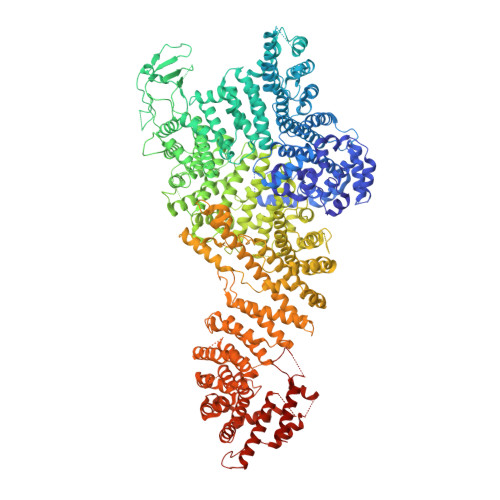
INTRODUCTION In eukaryotic cells, the selective bidirectional transport of macromolecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm occurs through the nuclear pore complex (NPC). Embedded in nuclear envelope pores, the ~110-MDa human NPC is an ~1200-Å-wide and ~750-Å-tall assembly of ~1000 proteins, collectively termed nucleoporins. Because of the NPC's eightfold rotational symmetry along the nucleocytoplasmic axis, each of the ~34 different nucleoporins occurs in multiples of eight. Architecturally, the NPC's symmetric core is composed of an inner ring encircling the central transport channel and two outer rings anchored on both sides of the nuclear envelope. Because of its central role in the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein, the NPC is commonly targeted in viral infections and its nucleoporin constituents are associated with a plethora of diseases. RATIONALE Although the arrangement of most scaffold nucleoporins in the NPC's symmetric core was determined by quantitative docking of crystal structures into cryo-electron tomographic (cryo-ET) maps of intact NPCs, the topology and molecular details of their cohesion by multivalent linker nucleoporins have remained elusive. Recently, in situ cryo-ET reconstructions of NPCs from various species have indicated that the NPC's inner ring is capable of reversible constriction and dilation in response to variations in nuclear envelope membrane tension, thereby modulating the diameter of the central transport channel by ~200 Å. We combined biochemical reconstitution, high-resolution crystal and single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure determination, docking into cryo-ET maps, and physiological validation to elucidate the molecular architecture of the linker-scaffold interaction network that not only is essential for the NPC's integrity but also confers the plasticity and robustness necessary to allow and withstand such large-scale conformational changes. RESULTS By biochemically mapping scaffold-binding regions of all fungal and human linker nucleoporins and determining crystal and single-particle cryo-EM structures of linker-scaffold complexes, we completed the characterization of the biochemically tractable linker-scaffold network and established its evolutionary conservation, despite considerable sequence divergence. We determined a series of crystal and single-particle cryo-EM structures of the intact Nup188 and Nup192 scaffold hubs bound to their Nic96, Nup145N, and Nup53 linker nucleoporin binding regions, revealing that both proteins form distinct question mark-shaped keystones of two evolutionarily conserved hetero‑octameric inner ring complexes. Linkers bind to scaffold surface pockets through short defined motifs, with flanking regions commonly forming additional disperse interactions that reinforce the binding. Using a structure‑guided functional analysis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae , we confirmed the robustness of linker‑scaffold interactions and established the physiological relevance of our biochemical and structural findings. The near-atomic composite structures resulting from quantitative docking of experimental structures into human and S. cerevisiae cryo-ET maps of constricted and dilated NPCs structurally disambiguated the positioning of the Nup188 and Nup192 hubs in the intact fungal and human NPC and revealed the topology of the linker-scaffold network. The linker-scaffold gives rise to eight relatively rigid inner ring spokes that are flexibly interconnected to allow for the formation of lateral channels. Unexpectedly, we uncovered that linker‑scaffold interactions play an opposing role in the outer rings by forming tight cross-link staples between the eight nuclear and cytoplasmic outer ring spokes, thereby limiting the dilatory movements to the inner ring. CONCLUSION We have substantially advanced the structural and biochemical characterization of the symmetric core of the S. cerevisiae and human NPCs and determined near-atomic composite structures. The composite structures uncover the molecular mechanism by which the evolutionarily conserved linker‑scaffold establishes the NPC's integrity while simultaneously allowing for the observed plasticity of the central transport channel. The composite structures are roadmaps for the mechanistic dissection of NPC assembly and disassembly, the etiology of NPC‑associated diseases, the role of NPC dilation in nucleocytoplasmic transport of soluble and integral membrane protein cargos, and the anchoring of asymmetric nucleoporins. [Figure: see text].
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, California Institute of Technology, 1200 East California Boulevard, Pasadena, CA 91125, USA.