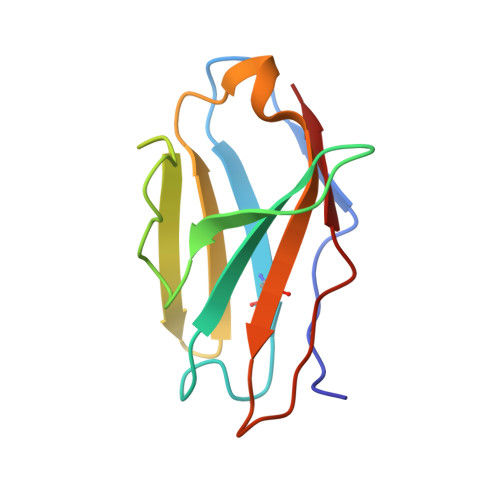
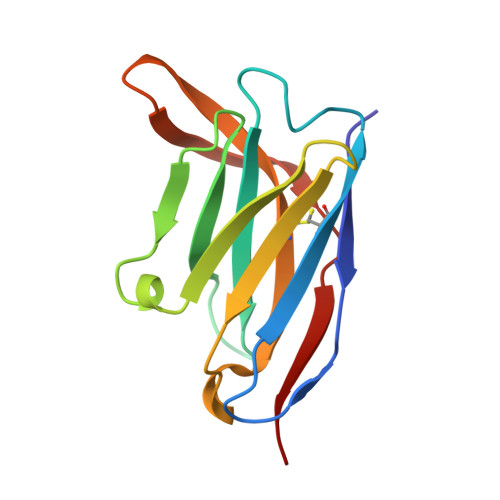
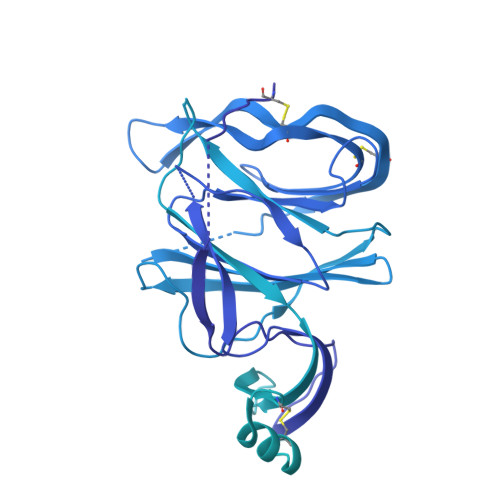
Molecular basis of immune evasion by the Delta and Kappa SARS-CoV-2 variants.
McCallum, M., Walls, A.C., Sprouse, K.R., Bowen, J.E., Rosen, L.E., Dang, H.V., De Marco, A., Franko, N., Tilles, S.W., Logue, J., Miranda, M.C., Ahlrichs, M., Carter, L., Snell, G., Pizzuto, M.S., Chu, H.Y., Van Voorhis, W.C., Corti, D., Veesler, D.(2021) Science 374: 1621-1626
- PubMed: 34751595
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abl8506
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7SO9, 7SOA, 7SOB, 7SOC, 7SOD, 7SOE, 7SOF - PubMed Abstract:
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) transmission leads to the emergence of variants, including the B.1.617.2 (Delta) variant of concern that is causing a new wave of infections and has become globally dominant. We show that these variants dampen the in vitro potency of vaccine-elicited serum neutralizing antibodies and provide a structural framework for describing their immune evasion. Mutations in the B.1.617.1 (Kappa) and Delta spike glycoproteins abrogate recognition by several monoclonal antibodies via alteration of key antigenic sites, including remodeling of the Delta amino-terminal domain. The angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 binding affinities of the Kappa and Delta receptor binding domains are comparable to the Wuhan-Hu-1 isolate, whereas B.1.617.2+ (Delta+) exhibits markedly reduced affinity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Washington, Seattle, WA 98195, USA.