Sensitive fluorogenic substrates for sirtuin deacylase inhibitor discovery.
Yang, L.L., Wang, H.L., Yan, Y.H., Liu, S., Yu, Z.J., Huang, M.Y., Luo, Y., Zheng, X., Yu, Y., Li, G.B.(2020) Eur J Med Chem 192: 112201-112201
- PubMed: 32163813
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112201
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
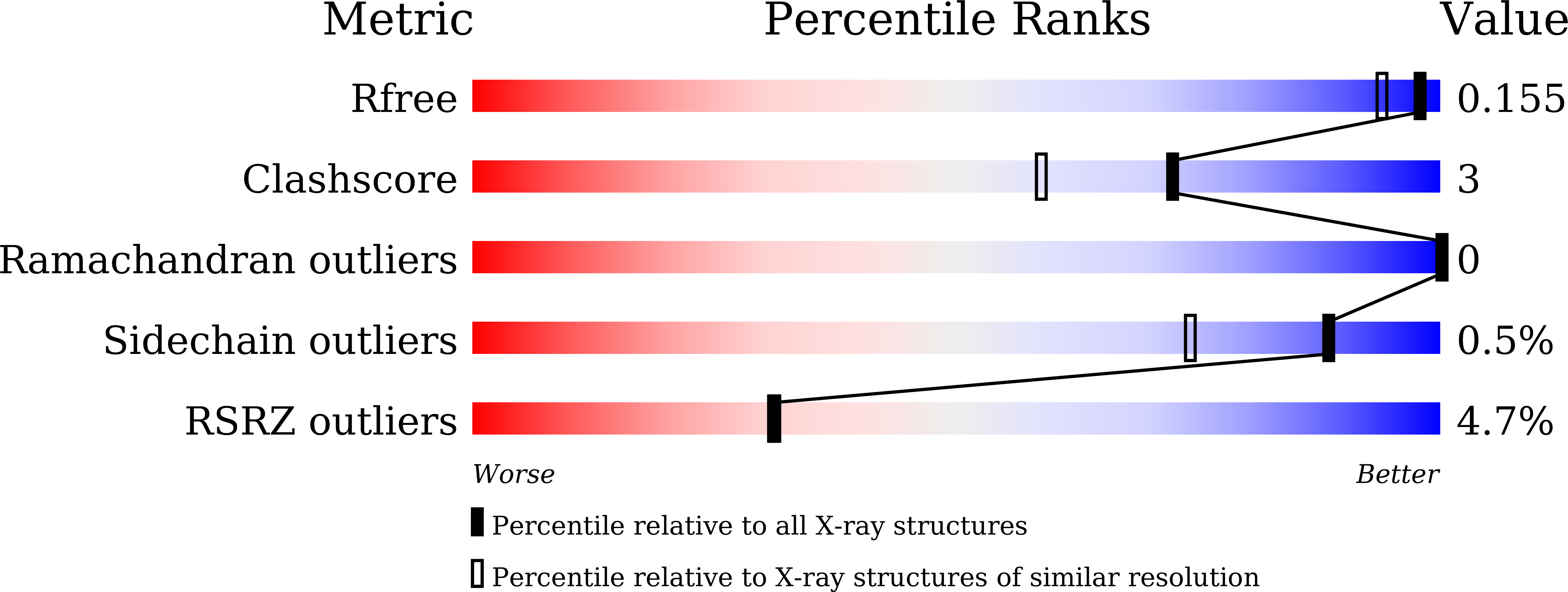
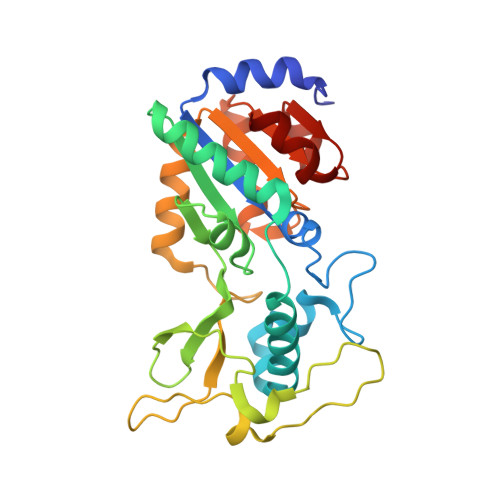
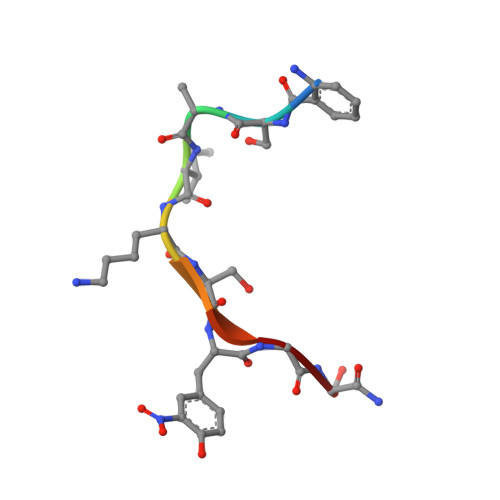
6LJK, 6LJM, 6LJN - PubMed Abstract:
Sirtuins (SIRTs) are NAD + -dependent lysine deacylases, regulating many important biological processes such as metabolism and stress responses. SIRT inhibitors may provide potential benefits against SIRT-driven human diseases. Development of efficient assay platforms based on fluorogenic substrates will facilitate the discovery of high-quality SIRT inhibitors. We here report 16 new fluorogenic peptide substrates (P1-P16) designed with structurally diverse tetrapeptides and acyl modifications. Tests of P1-P16 against SIRT isoforms identified several sensitive substrates for SIRT1, SIRT2, SIRT3 and SIRT5, which manifested lower K M values and higher catalytic efficiency, and particularly had less signal interference in inhibitor screening compared with our previously reported internally quenched fluorescent substrates. Co-crystallization of sensitive substrates P13 and P15 with SIRT5 revealed an unexpected binding mode, involving interactions with residues from active site bordering surfaces, different from that observed for other peptides derived from natural protein substrates. By using SIRT5 sensitive substrates, we found that TW-37, a Bcl-2 inhibitor, displayed low micromolar inhibition to SIRT5, which was further validated by isothermal titration calorimetry analyses, offering a new point to develop dual-action SIRT5/Bcl-2 inhibitors against cancers. This work provides assay platform and structural basis for developing new substrates and inhibitors targeting human SIRTs.
Organizational Affiliation:
College of Food and Bioengineering, Xihua University, Sichuan, 610039, PR China.