Cardiac hypertrophy and arrhythmia in mice induced by a mutation in ryanodine receptor 2.
Alvarado, F.J., Bos, J.M., Yuchi, Z., Valdivia, C.R., Hernandez, J.J., Zhao, Y.T., Henderlong, D.S., Chen, Y., Booher, T.R., Marcou, C.A., Van Petegem, F., Ackerman, M.J., Valdivia, H.H.(2019) JCI Insight 5
- PubMed: 30835254
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.126544
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
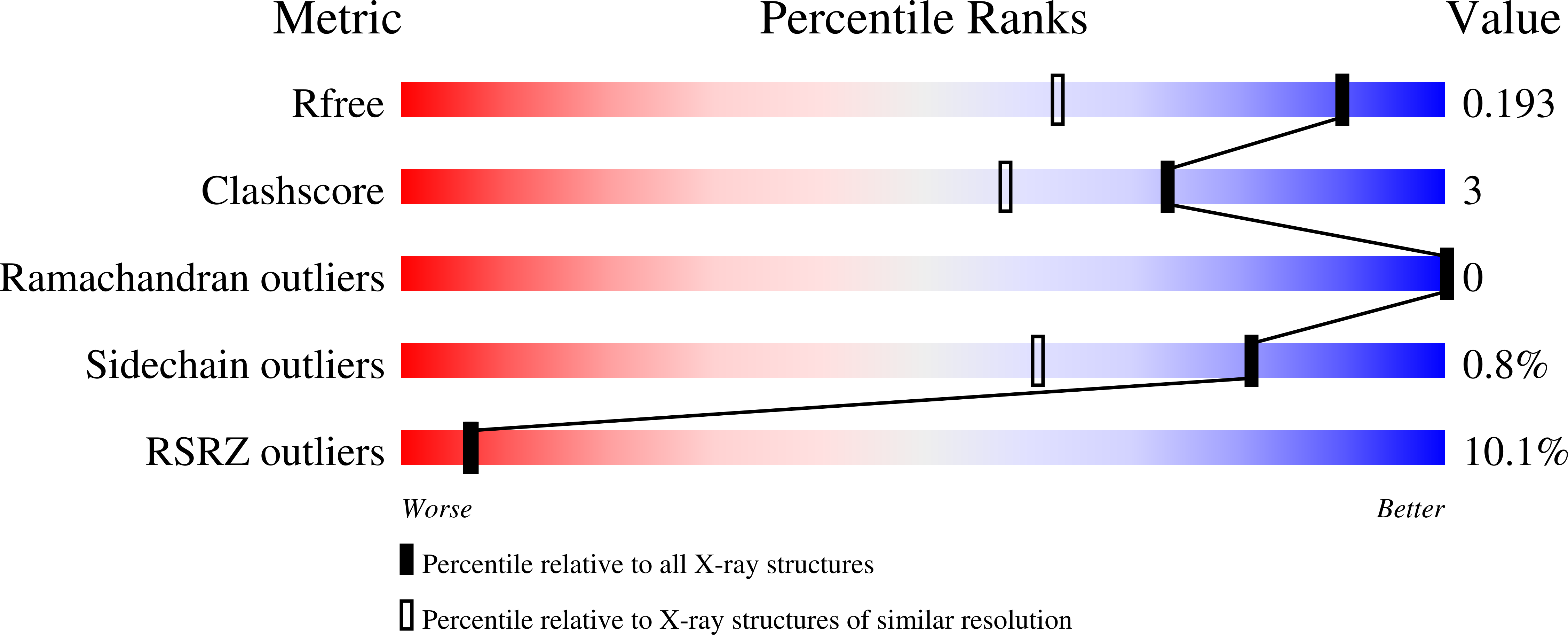
5VSN - PubMed Abstract:
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is triggered mainly by mutations in genes encoding sarcomeric proteins, but a significant proportion of patients lack a genetic diagnosis. We identified a novel mutation in the ryanodine receptor 2, RyR2-P1124L, in a patient from a genotype-negative HCM cohort. The aim of this study was to determine whether RyR2-P1124L triggers functional and structural alterations in isolated RyR2 channels and whole hearts. We found that P1124L induces significant conformational changes in the SPRY2 domain of RyR2. Recombinant RyR2-P1124L channels displayed a cytosolic loss-of-function phenotype, which contrasted with a higher sensitivity to luminal [Ca2+], indicating a luminal gain-of-function. Homozygous mice for RyR2-P1124L showed mild cardiac hypertrophy, similar to the human patient. This phenotype, evident at 1 yr of age, was accompanied by an increase in the expression of calmodulin (CaM). P1124L mice also showed higher susceptibility to arrhythmia at 8 mo of age, before the onset of hypertrophy. RyR2-P1124L has a distinct cytosolic loss-of-function and a luminal gain-of-function phenotype. This bifunctionally-divergent behavior triggers arrhythmias and structural cardiac remodeling, and involves overexpression of calmodulin as a potential hypertrophic mediator. This study is relevant to continue elucidating the possible causes of genotype-negative HCM and the role of RyR2 in cardiac hypertrophy.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Medicine, Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, and Cardiovascular Research Center, University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, Wisconsin, USA.