Crystal structures of murine and human Histamine-Releasing Factor (HRF/TCTP) and a model for HRF dimerisation in mast cell activation.
Dore, K.A., Kashiwakura, J.I., McDonnell, J.M., Gould, H.J., Kawakami, T., Sutton, B.J., Davies, A.M.(2017) Mol Immunol 93: 216-222
- PubMed: 29216544
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2017.11.022
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
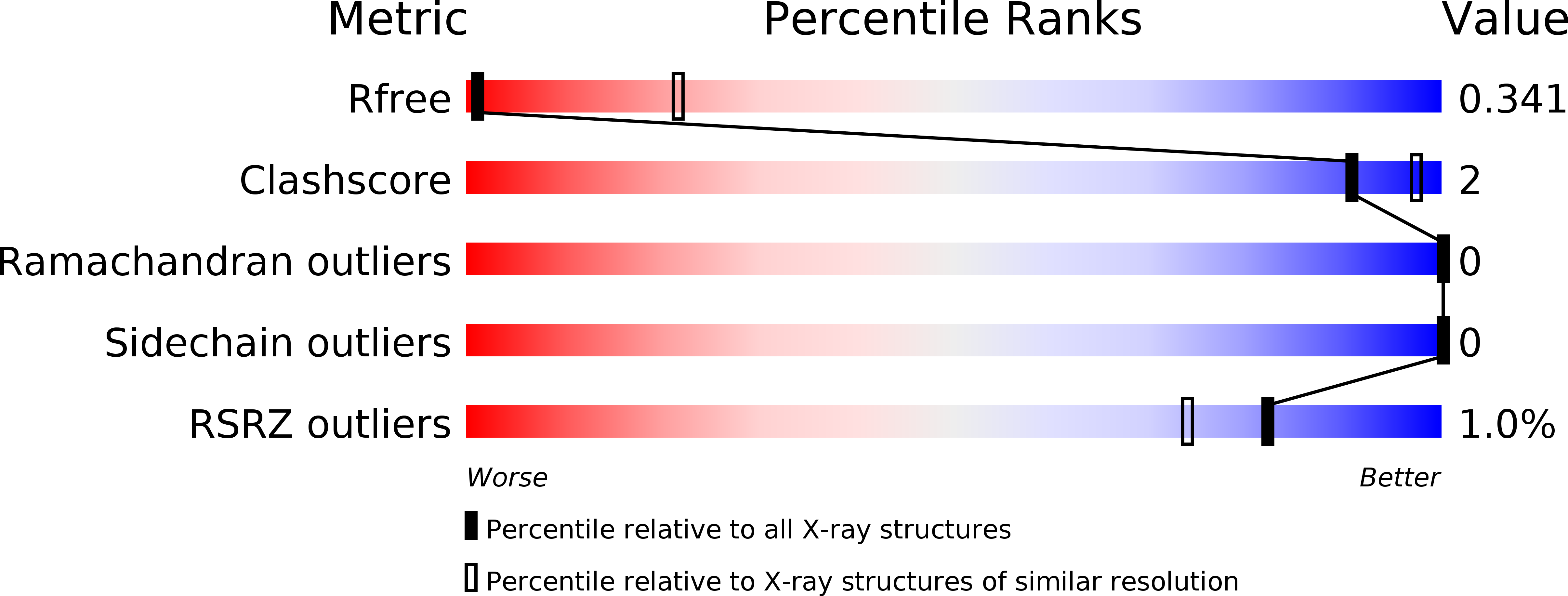
5O9K, 5O9L, 5O9M - PubMed Abstract:
In allergic disease, mast cell activation is conventionally triggered by allergen-mediated cross-linking of receptor-bound IgE on the cell surface. In addition to its diverse range of intracellular roles in apoptosis, cell proliferation and cancer, Histamine-Releasing Factor (HRF) also activates mast cells and basophils. A subset of IgE antibodies bind HRF through their Fab regions, and two IgE binding sites on HRF have been mapped. HRF can form dimers, and a disulphide-linked dimer is critical for activity. The current model for the activity of HRF in mast cell activation involves cross-linking of receptor-bound IgE by dimeric HRF, mediated by HRF/Fab interactions. HRF crystal and solution structures have provided little insight into either the formation of disulphide-linked HRF dimers or the ability of HRF to activate mast cells. We report the first crystal structure of murine HRF (mHRF) to 4.0Å resolution, revealing a conserved fold. We also solved the structure of human HRF (hHRF) in two new crystal forms, one at the highest resolution (1.4Å) yet reported. The high resolution hHRF structure reveals a disulphide-linked dimer, in which the two molecules are closely associated, and provides a model for the role of both human and murine HRF in mast cell activation.
Organizational Affiliation:
King's College London, Randall Centre for Cell and Molecular Biophysics, New Hunt's House, London, SE1 1UL, United Kingdom; Medical Research Council & Asthma UK Centre in Allergic Mechanisms of Asthma, London, United Kingdom.