Reader domain specificity and lysine demethylase-4 family function.
Su, Z., Wang, F., Lee, J.H., Stephens, K.E., Papazyan, R., Voronina, E., Krautkramer, K.A., Raman, A., Thorpe, J.J., Boersma, M.D., Kuznetsov, V.I., Miller, M.D., Taverna, S.D., Phillips, G.N., Denu, J.M.(2016) Nat Commun 7: 13387-13387
- PubMed: 27841353
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13387
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4UC4, 5D6W, 5D6X, 5D6Y - PubMed Abstract:
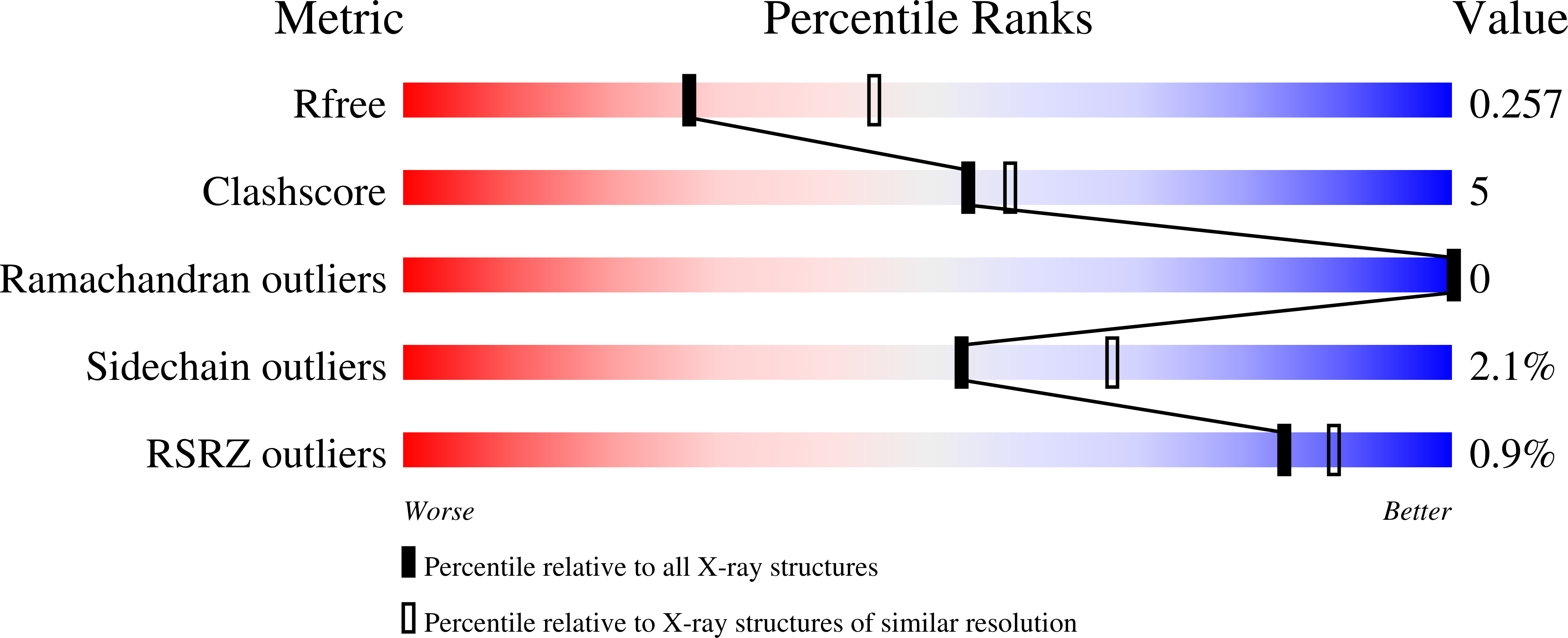
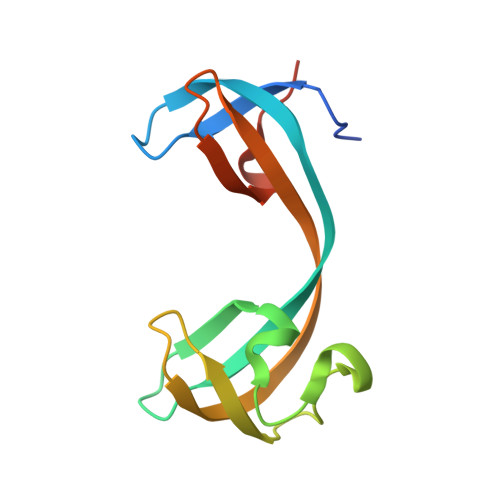
The KDM4 histone demethylases are conserved epigenetic regulators linked to development, spermatogenesis and tumorigenesis. However, how the KDM4 family targets specific chromatin regions is largely unknown. Here, an extensive histone peptide microarray analysis uncovers trimethyl-lysine histone-binding preferences among the closely related KDM4 double tudor domains (DTDs). KDM4A/B DTDs bind strongly to H3K23me3, a poorly understood histone modification recently shown to be enriched in meiotic chromatin of ciliates and nematodes. The 2.28 Å co-crystal structure of KDM4A-DTD in complex with H3K23me3 peptide reveals key intermolecular interactions for H3K23me3 recognition. Furthermore, analysis of the 2.56 Å KDM4B-DTD crystal structure pinpoints the underlying residues required for exclusive H3K23me3 specificity, an interaction supported by in vivo co-localization of KDM4B and H3K23me3 at heterochromatin in mammalian meiotic and newly postmeiotic spermatocytes. In vitro demethylation assays suggest H3K23me3 binding by KDM4B stimulates H3K36 demethylation. Together, these results provide a possible mechanism whereby H3K23me3-binding by KDM4B directs localized H3K36 demethylation during meiosis and spermatogenesis.
Organizational Affiliation:
Wisconsin Institute for Discovery, Morgridge Institute for Research, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, Wisconsin 53715, USA.