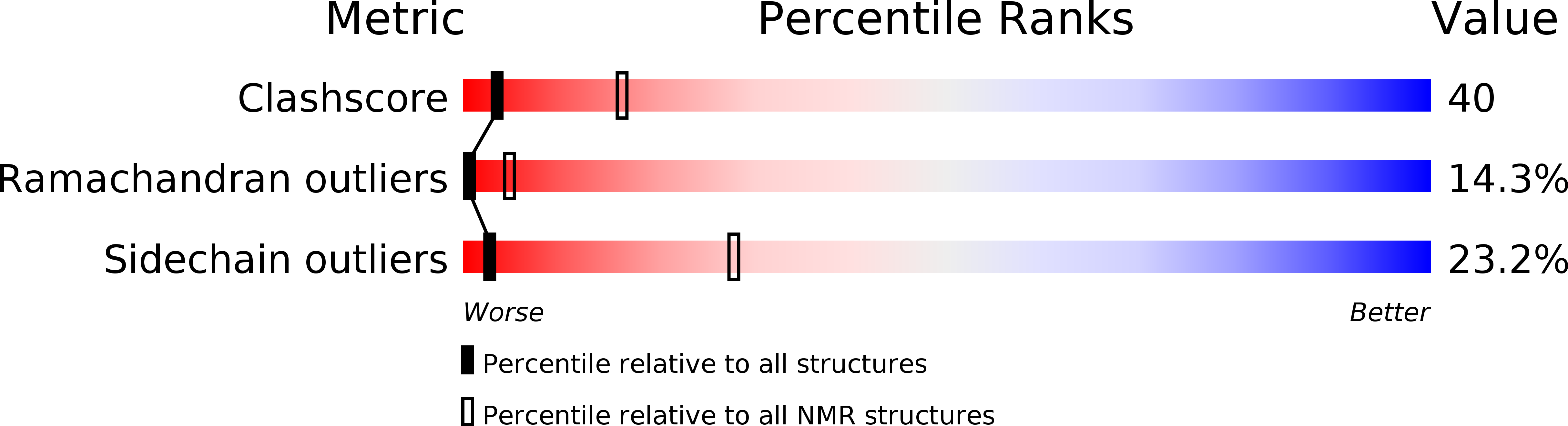Barley lipid-transfer protein complexed with palmitoyl CoA: the structure reveals a hydrophobic binding site that can expand to fit both large and small lipid-like ligands.
Lerche, M.H., Kragelund, B.B., Bech, L.M., Poulsen, F.M.(1997) Structure 5: 291-306
- PubMed: 9032083
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(97)00186-x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1JTB - PubMed Abstract:
. Plant nonspecific lipid-transfer proteins (nsLTPs) bind a variety of very different lipids in vitro, including phospholipids, glycolipids, fatty acids and acyl coenzyme As. In this study we have determined the structure of a nsLTP complexed with palmitoyl coenzyme A (PCoA) in order to further our understanding of the structural mechanism of the broad specificity of these proteins and its relation to the function of nsLTPs in vivo. . 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) have been used to study the complex between a nsLTP isolated from barley seeds (bLTP) and the ligand PCoA. The resonances of 97% of the 1H atoms were assigned for the complexed bLTP and nearly all of the resonances were assigned in the bound PCoA ligand. The palmitoyl chain of the ligand was uniformly 13C-labelled allowing the two ends of the hydrocarbon chain to be assigned. The comparison of a subset of 20 calculated structures to an average structure showed root mean square deviations of 1.89 +/- 0.19 for all C, N, O, P and S atoms of the entire complex and of 0.57 +/- 0.09 for the peptide backbone atoms of the four alpha helices of the complexed bLTP. The four-helix topology of the uncomplexed bLTP is maintained in the complexed form of the protein. The bLTP only binds the hydrophobic parts of PCoA with the rest of the ligand remaining exposed to the solvent. The palmitoyl chain moiety of the ligand is placed in the interior of the protein and bent in a U-shape. This part of the ligand is completely buried within a hydrophobic pocket of the protein. . A comparison of the structures of bLTP in the free and bound forms suggests that bLTP can accommodate long olefinic ligands by expansion of the hydrophobic binding site. This expansion is achieved by a bend of one helix, HA, and by conformational changes in both the C terminus and helix HC. This mode of binding is different from that seen in the structure of maize nsLTP in complex with palmitic acid, where binding of the ligand is not associated with structural changes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Carlsberg Laboratorium, Kemisk Afdeling, Gamle Carlsberg Vej 10, DK-2500 Valby, Copenhagen, Denmark.