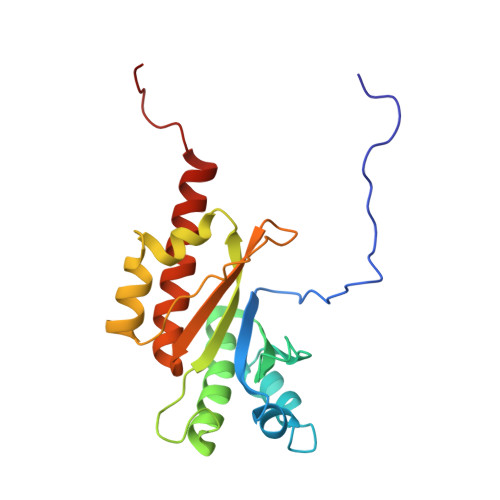
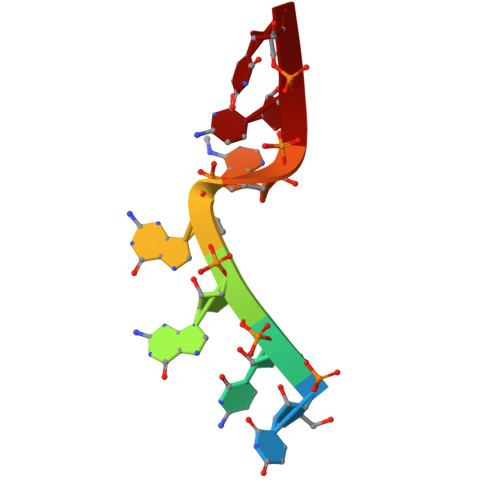
Direct m6A recognition by IMP1 underlays an alternative model of target selection for non-canonical methyl-readers.
Nicastro, G., Abis, G., Klein, P., Esteban-Serna, S., Gallagher, C., Chaves-Arquero, B., Cai, Y., Figueiredo, A.M., Martin, S.R., Patani, R., Taylor, I.A., Ramos, A.(2023) Nucleic Acids Res 51: 8774-8786
- PubMed: 37377445
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkad534
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8COO - PubMed Abstract:
m6A methylation provides an essential layer of regulation in organismal development, and is aberrant in a range of cancers and neuro-pathologies. The information encoded by m6A methylation is integrated into existing RNA regulatory networks by RNA binding proteins that recognise methylated sites, the m6A readers. m6A readers include a well-characterised class of dedicated proteins, the YTH proteins, as well as a broader group of multi-functional regulators where recognition of m6A is only partially understood. Molecular insight in this recognition is essential to build a mechanistic understanding of global m6A regulation. In this study, we show that the reader IMP1 recognises the m6A using a dedicated hydrophobic platform that assembles on the methyl moiety, creating a stable high-affinity interaction. This recognition is conserved across evolution and independent from the underlying sequence context but is layered upon the strong sequence specificity of IMP1 for GGAC RNA. This leads us to propose a concept for m6A regulation where methylation plays a context-dependent role in the recognition of selected IMP1 targets that is dependent on the cellular concentration of available IMP1, differing from that observed for the YTH proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Macromolecular Structure Laboratory, The Francis Crick Institute, 1 Midland Road, London NW1 1AT, UK.