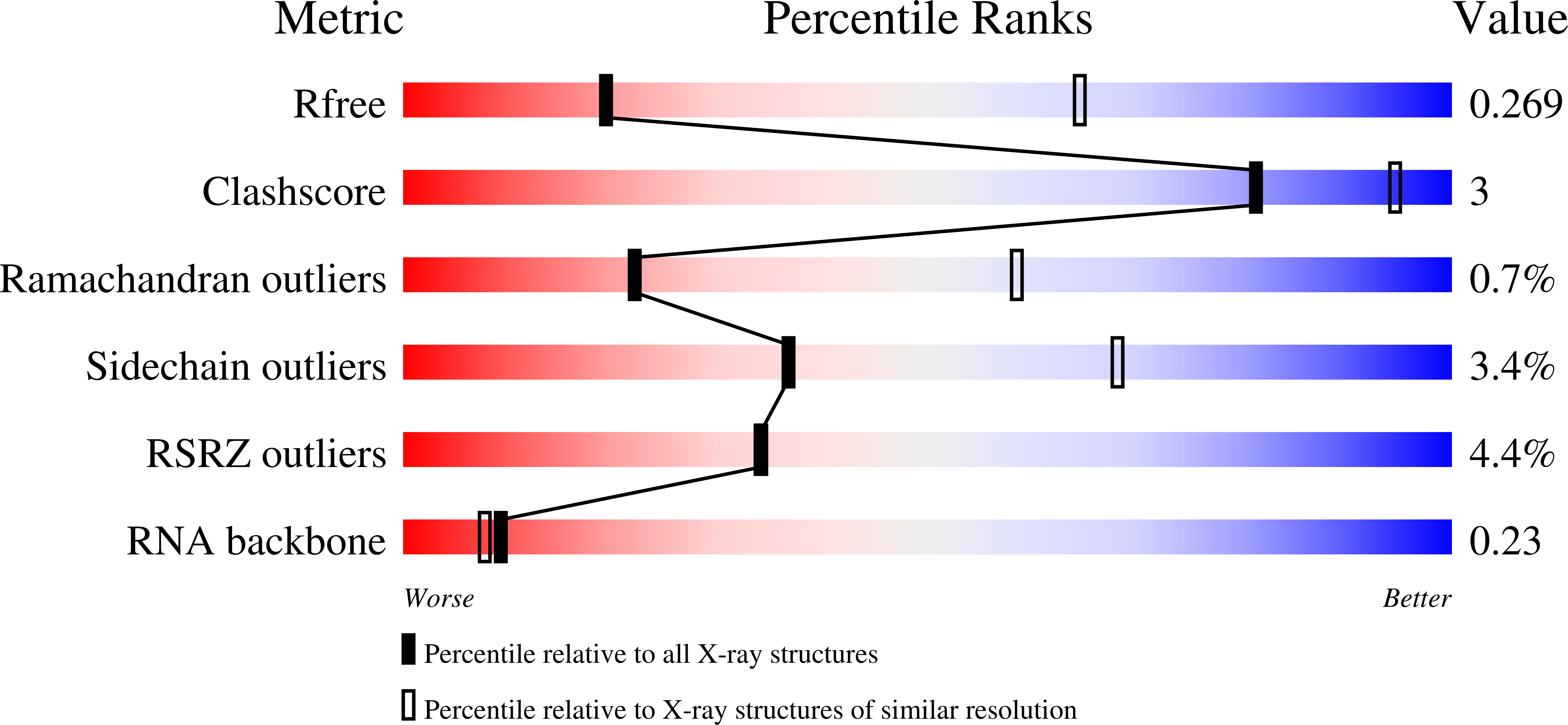
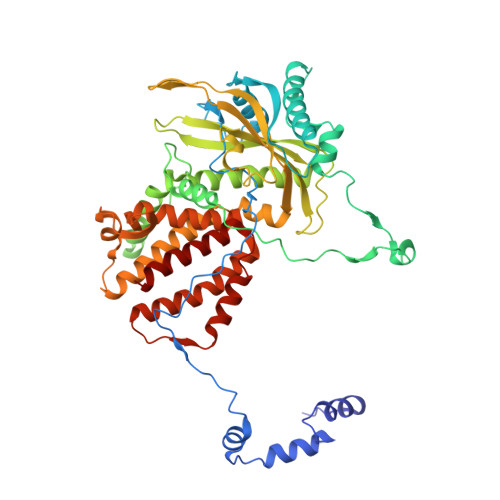
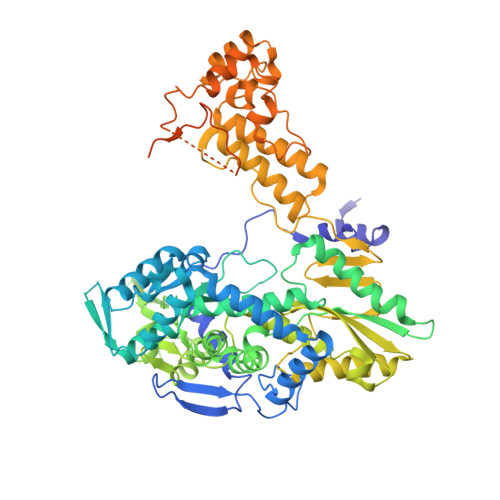
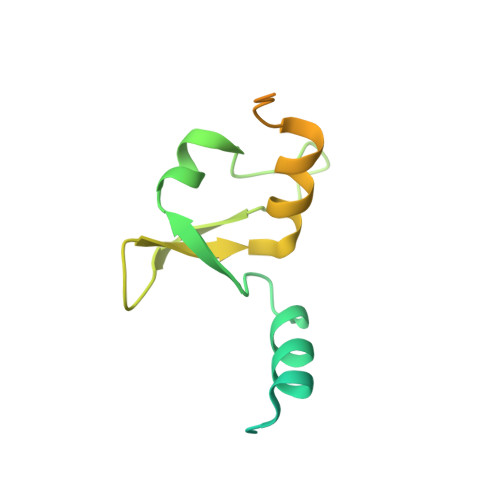
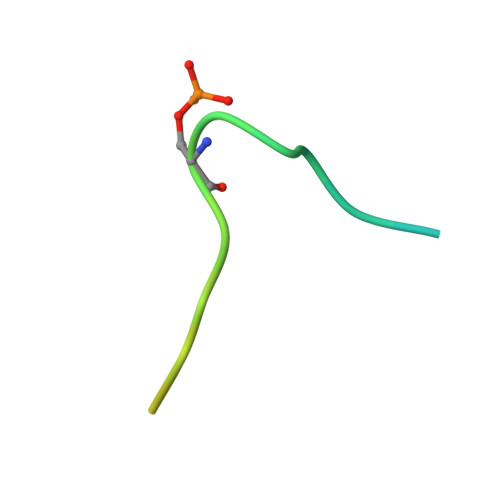
Type B and type A influenza polymerases have evolved distinct binding interfaces to recruit the RNA polymerase II CTD.
Krischuns, T., Isel, C., Drncova, P., Lukarska, M., Pflug, A., Paisant, S., Navratil, V., Cusack, S., Naffakh, N.(2022) PLoS Pathog 18: e1010328-e1010328
- PubMed: 35605026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1010328
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7Z42, 7Z43, 7Z4O - PubMed Abstract:
During annual influenza epidemics, influenza B viruses (IBVs) co-circulate with influenza A viruses (IAVs), can become predominant and cause severe morbidity and mortality. Phylogenetic analyses suggest that IAVs (primarily avian viruses) and IBVs (primarily human viruses) have diverged over long time scales. Identifying their common and distinctive features is an effective approach to increase knowledge about the molecular details of influenza infection. The virus-encoded RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (FluPolB and FluPolA) are PB1-PB2-PA heterotrimers that perform transcription and replication of the viral genome in the nucleus of infected cells. Initiation of viral mRNA synthesis requires a direct association of FluPol with the host RNA polymerase II (RNAP II), in particular the repetitive C-terminal domain (CTD) of the major RNAP II subunit, to enable "cap-snatching" whereby 5'-capped oligomers derived from nascent RNAP II transcripts are pirated to prime viral transcription. Here, we present the first high-resolution co-crystal structure of FluPolB bound to a CTD mimicking peptide at a binding site crossing from PA to PB2. By performing structure-based mutagenesis of FluPolB and FluPolA followed by a systematic investigation of FluPol-CTD binding, FluPol activity and viral phenotype, we demonstrate that IBVs and IAVs have evolved distinct binding interfaces to recruit the RNAP II CTD, despite the CTD sequence being highly conserved across host species. We find that the PB2 627 subdomain, a major determinant of FluPol-host cell interactions and IAV host-range, is involved in CTD-binding for IBVs but not for IAVs, and we show that FluPolB and FluPolA bind to the host RNAP II independently of the CTD. Altogether, our results suggest that the CTD-binding modes of IAV and IBV may represent avian- and human-optimized binding modes, respectively, and that their divergent evolution was shaped by the broader interaction network between the FluPol and the host transcriptional machinery.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institut Pasteur, Université Paris Cité, CNRS UMR3569, Unité Biologie des ARN et Virus Influenza, Paris, France.