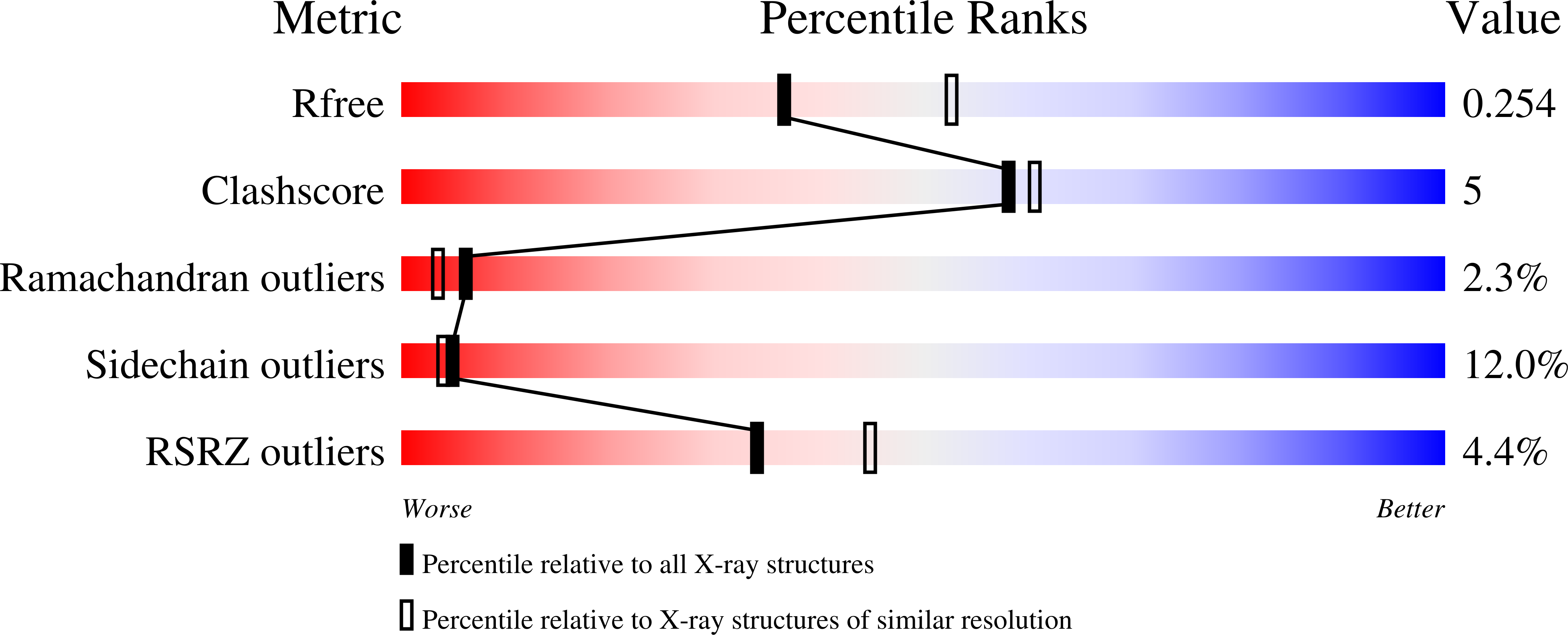
Discovery and characterization of UipA, a uranium- and iron-binding PepSY protein involved in uranium tolerance by soil bacteria.
Gallois, N., Alpha-Bazin, B., Bremond, N., Ortet, P., Barakat, M., Piette, L., Mohamad Ali, A., Lemaire, D., Legrand, P., Theodorakopoulos, N., Floriani, M., Fevrier, L., Den Auwer, C., Arnoux, P., Berthomieu, C., Armengaud, J., Chapon, V.(2022) ISME J 16: 705-716
- PubMed: 34556817
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-021-01113-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7ATH, 7ATK - PubMed Abstract:
Uranium is a naturally occurring radionuclide. Its redistribution, primarily due to human activities, can have adverse effects on human and non-human biota, which poses environmental concerns. The molecular mechanisms of uranium tolerance and the cellular response induced by uranium exposure in bacteria are not yet fully understood. Here, we carried out a comparative analysis of four actinobacterial strains isolated from metal and radionuclide-rich soils that display contrasted uranium tolerance phenotypes. Comparative proteogenomics showed that uranyl exposure affects 39-47% of the total proteins, with an impact on phosphate and iron metabolisms and membrane proteins. This approach highlighted a protein of unknown function, named UipA, that is specific to the uranium-tolerant strains and that had the highest positive fold-change upon uranium exposure. UipA is a single-pass transmembrane protein and its large C-terminal soluble domain displayed a specific, nanomolar binding affinity for UO 2 2+ and Fe 3+ . ATR-FTIR and XAS-spectroscopy showed that mono and bidentate carboxylate groups of the protein coordinated both metals. The crystal structure of UipA, solved in its apo state and bound to uranium, revealed a tandem of PepSY domains in a swapped dimer, with a negatively charged face where uranium is bound through a set of conserved residues. This work reveals the importance of UipA and its PepSY domains in metal binding and radionuclide tolerance.
Organizational Affiliation:
Aix Marseille Université, CEA, CNRS, BIAM, 13108, Saint Paul-Lez-Durance, France.