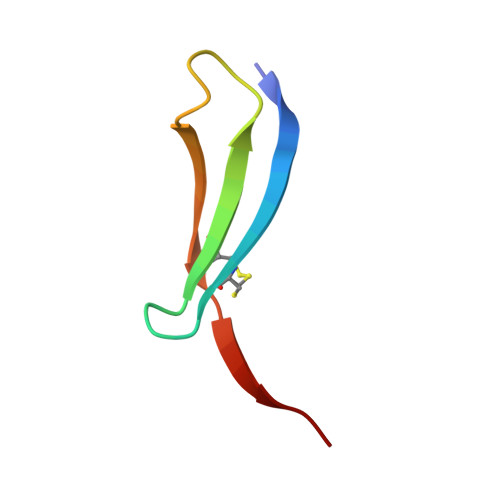
Core fucose-specific Pholiota squarrosa lectin (PhoSL) as a potent broad-spectrum inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Yamasaki, K., Adachi, N., Ngwe Tun, M.M., Ikeda, A., Moriya, T., Kawasaki, M., Yamasaki, T., Kubota, T., Nagashima, I., Shimizu, H., Tateno, H., Morita, K.(2023) FEBS J 290: 412-427
- PubMed: 36007953
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.16599
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7VU9 - PubMed Abstract:
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike protein (S protein) is highly N-glycosylated, and a "glycan shield" is formed to limit the access of other molecules; however, a small open area coincides with the interface to the host's receptor and also neutralising antibodies. Most of the variants of concern have mutations in this area, which could reduce the efficacy of existing antibodies. In contrast, N-glycosylation sites are relatively invariant, and some are essential for infection. Here, we observed that the S proteins of the ancestral (Wuhan) and Omicron strains bind with Pholiota squarrosa lectin (PhoSL), a 40-amino-acid chemically synthesised peptide specific to core-fucosylated N-glycans. The affinities were at a low nanomolar level, which were ~ 1000-fold stronger than those between PhoSL and the core-fucosylated N-glycans at the micromolar level. We demonstrated that PhoSL inhibited infection by both strains at similar submicromolar levels, suggesting its broad-spectrum effect on SARS-CoV-2 variants. Cryogenic electron microscopy revealed that PhoSL caused an aggregation of the S protein, which was likely due to the multivalence of both the trimeric PhoSL and S protein. This characteristic is likely relevant to the inhibitory mechanism. Structural modelling of the PhoSL-S protein complex indicated that PhoSL was in contact with the amino acids of the S protein, which explains the enhanced affinity with S protein and also indicates the significant potential for developing specific binders by the engineering of PhoSL.
Organizational Affiliation:
Biomedical Research Institute, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Tsukuba, Japan.