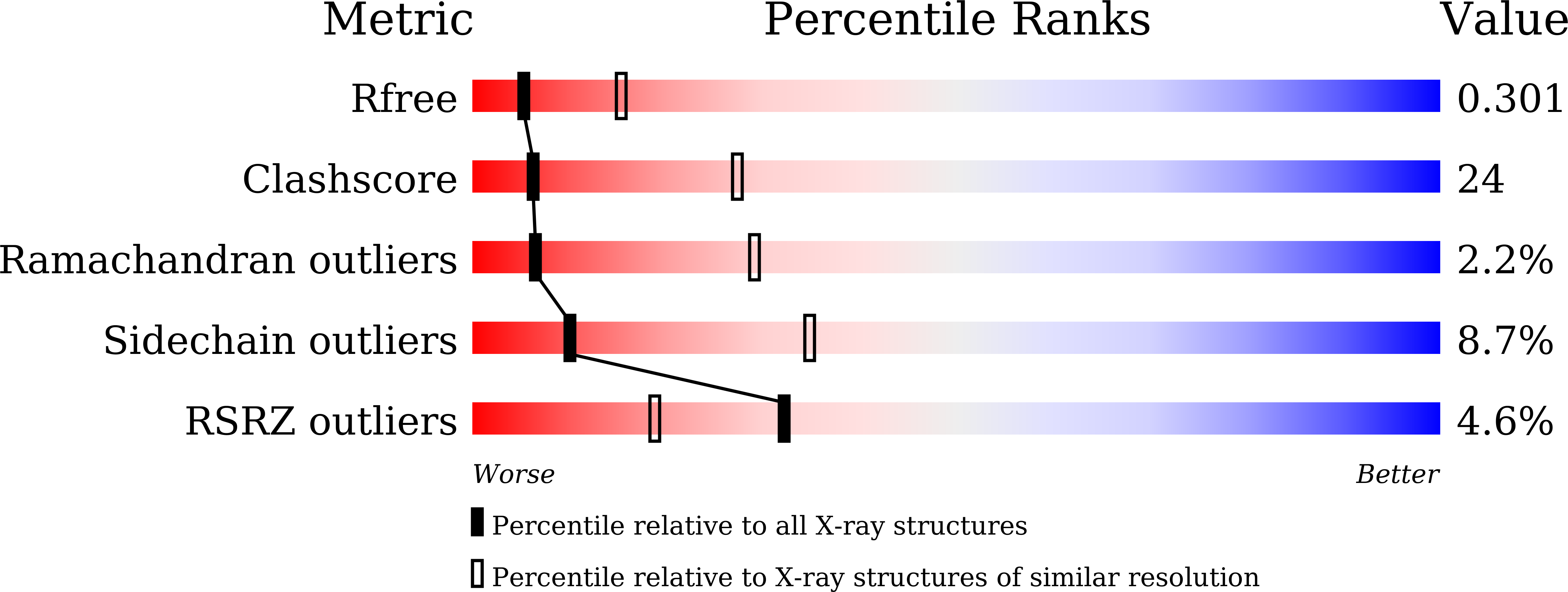
Crystal structure of the nucleoid-associated protein Fis (PA4853) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Zhou, J., Gao, Z., Zhang, H., Dong, Y.(2020) Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun 76: 209-215
- PubMed: 32356522
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053230X20005427
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6M10 - PubMed Abstract:
Factor for inversion stimulation (Fis) is a versatile bacterial nucleoid-associated protein that can directly bind and bend DNA to influence DNA topology. It also plays crucial roles in regulating bacterial virulence factors and in optimizing bacterial adaptation to various environments. Fis from Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA4853, referred to as PaFis) has recently been found to be required for virulence by regulating the expression of type III secretion system (T3SS) genes. PaFis can specifically bind to the promoter region of exsA, which functions as a T3SS master regulator, to regulate its expression and plays an essential role in transcription elongation from exsB to exsA. Here, the crystal structure of PaFis, which is composed of a four-helix bundle and forms a homodimer, is reported. PaFis shows remarkable structural similarities to the well studied Escherichia coli Fis (EcFis), including an N-terminal flexible loop and a C-terminal helix-turn-helix (HTH) motif. However, the critical residues for Hin-catalyzed DNA inversion in the N-terminal loop of EcFis are not conserved in PaFis and further studies are required to investigate its exact role. A gel-electrophoresis mobility-shift assay showed that PaFis can efficiently bind to the promoter region of exsA. Structure-based mutagenesis revealed that several conserved basic residues in the HTH motif play essential roles in DNA binding. These structural and biochemical studies may help in understanding the role of PaFis in the regulation of T3SS expression and in virulence.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Health Sciences and School of Life Science, Anhui University, Hefei, Anhui 230601, People's Republic of China.